 Jan Kieseler is an experimental particle physicist working at the interface of fundamental research and advanced technologies. His work focuses on top quark and Higgs boson interactions, detector optimization, and machine learning in reconstruction and computing. At KIT, he teaches courses in modern particle physics and data analysis, and supervises Bachelor, Master, and PhD students on topics ranging from collider physics to AI-driven detector design.
Jan Kieseler is an experimental particle physicist working at the interface of fundamental research and advanced technologies. His work focuses on top quark and Higgs boson interactions, detector optimization, and machine learning in reconstruction and computing. At KIT, he teaches courses in modern particle physics and data analysis, and supervises Bachelor, Master, and PhD students on topics ranging from collider physics to AI-driven detector design.
Contact:
Jan Kieseler (he/him)
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Institute of Experimental Particle Physics (ETP)
Office: Building 30.23, Room 9-6
Office hours: by appointment only
Email:
jan.kieseler@kit.edu
In the following, you can find the latest news, publications, talks and activities with collaborators and students.
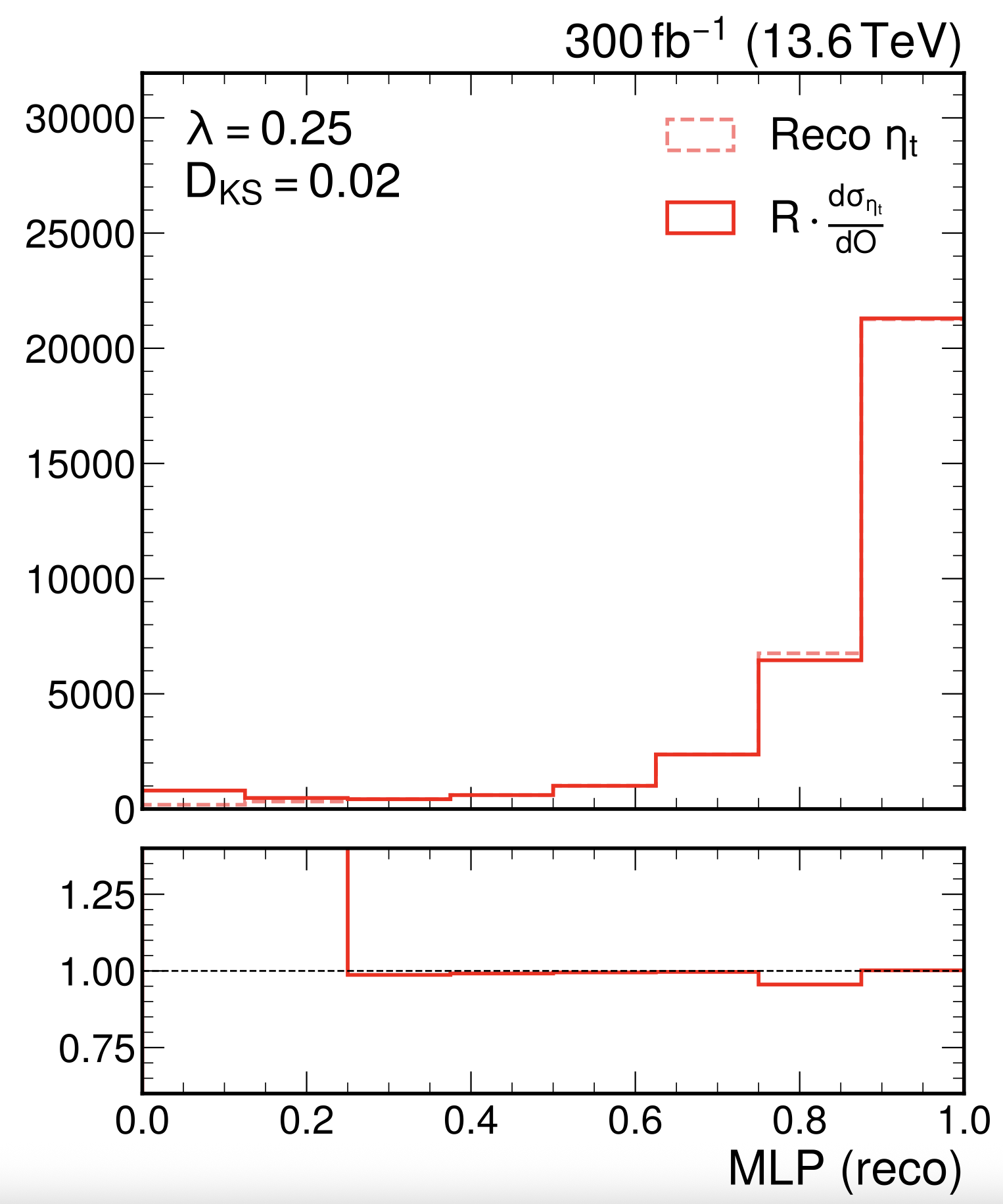
Torben Mohr, et al.:
We present the Optimal Observable Machine (OOM), a machine-learning framework that learns unfoldable generator-level observables tailored to maximize sensitivity to a parameter of interest while incorporating detector response and systematic uncertainties. Demonstrated in a top quark physics case study, OOM yields observables with enhanced sensitivity and long-term reinterpretability compared to traditional approaches.
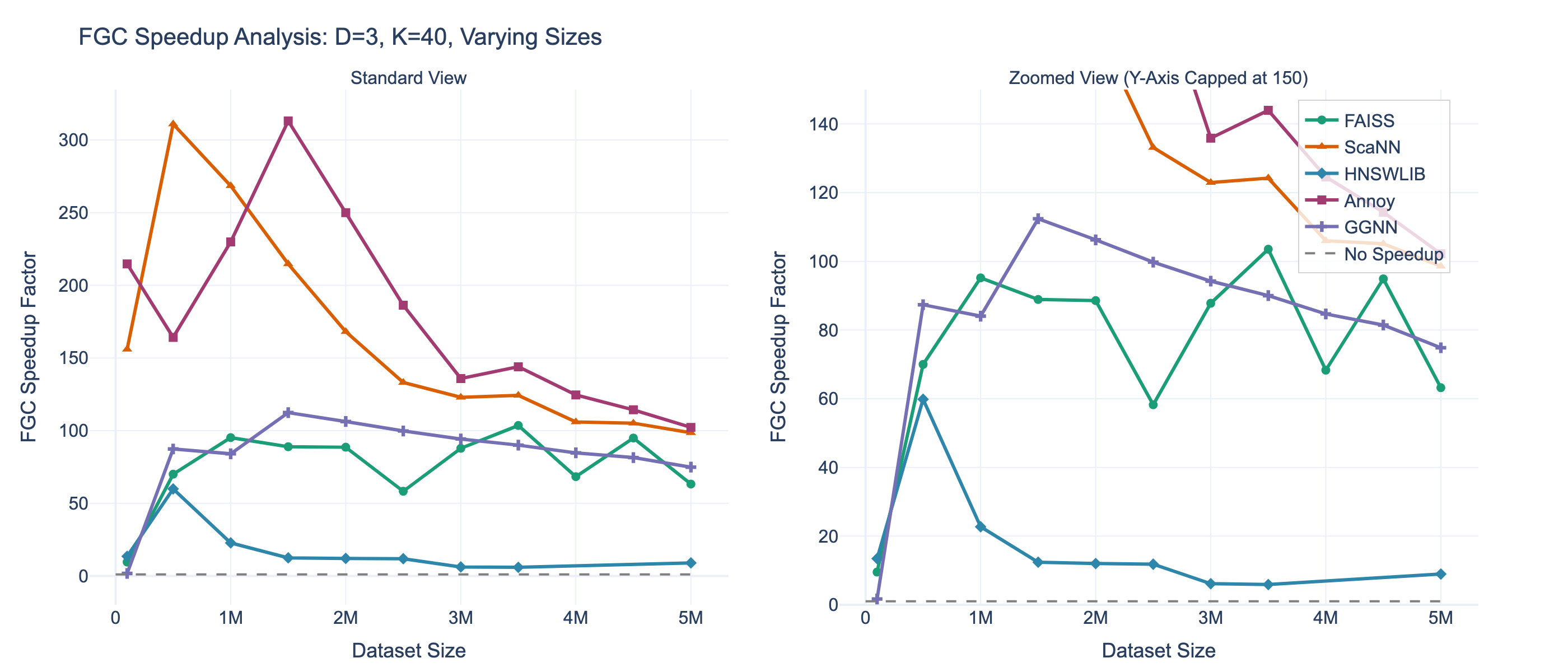
Aarush Agarwal, et al.:
FastGraph introduces a GPU-optimized method for building hit-connection graphs up to 300 times faster than existing approaches—without added memory overhead. This dramatically accelerates graph-based particle-reconstruction workflows and enables more ambitious machine-learning models for detector data.
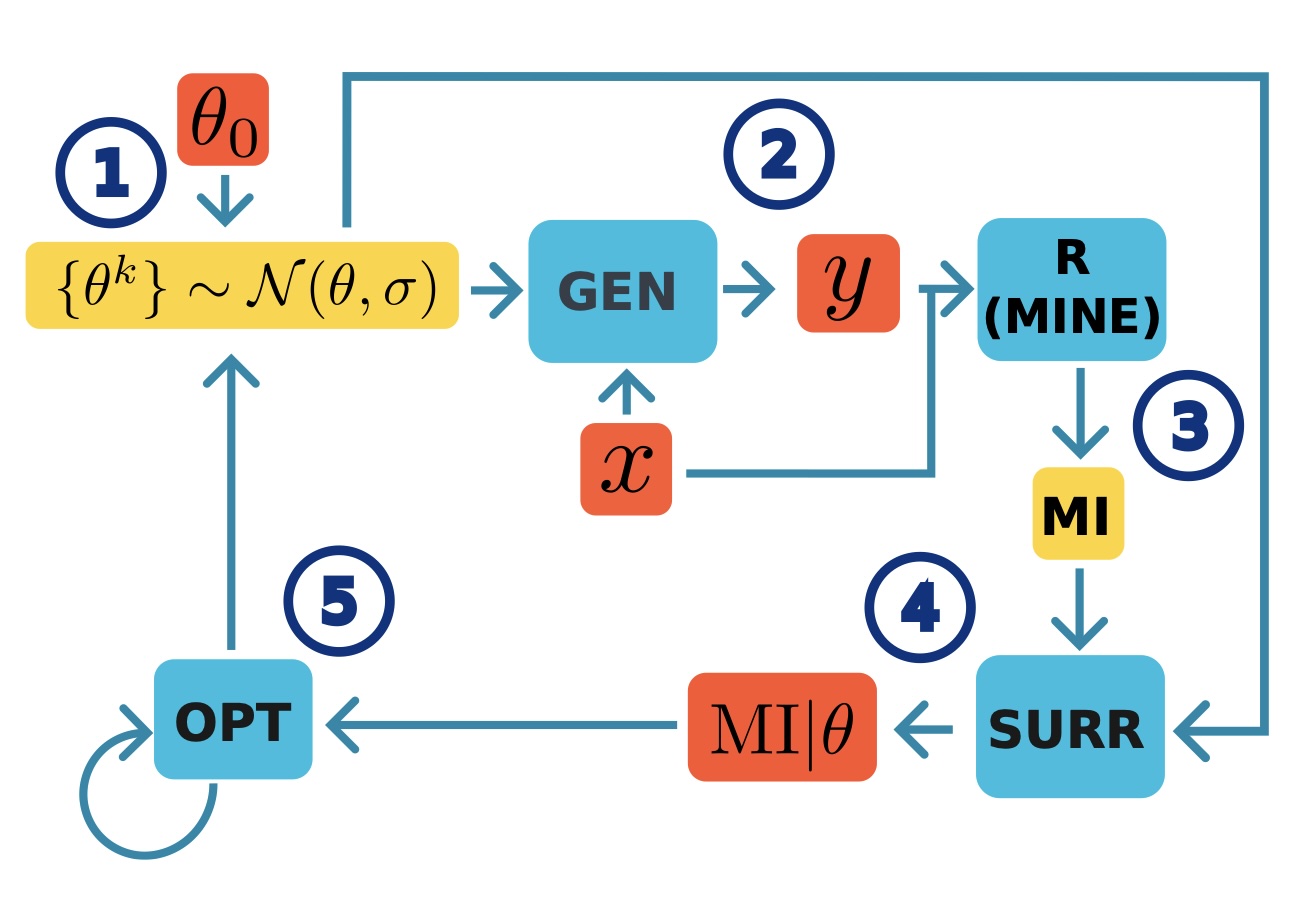
Kinga Wozniak, et al.:
We introduce an AI-powered method that lets a computer optimise particle-detector layouts and quickly learn which designs capture the most useful information. Using a measure from information theory called mutual information, the approach finds detector configurations that match—or even beat—today’s best hand-tuned designs while requiring far less expert tweaking.
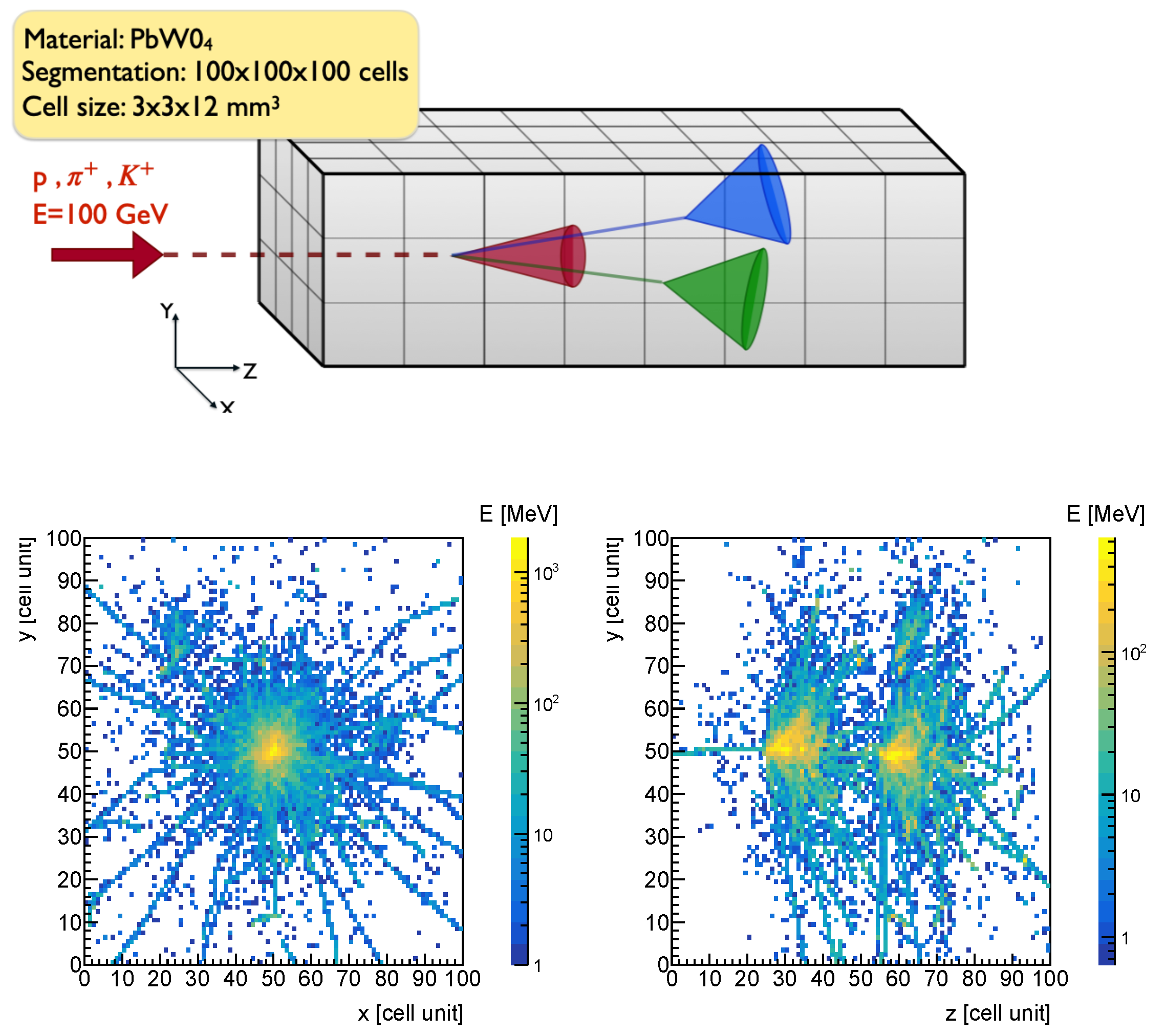
Andrea De Vita, et al.:
We explore the potential of highly granular calorimeters for hadron identification, highlighting the role of advanced machine learning techniques in enhancing performance.
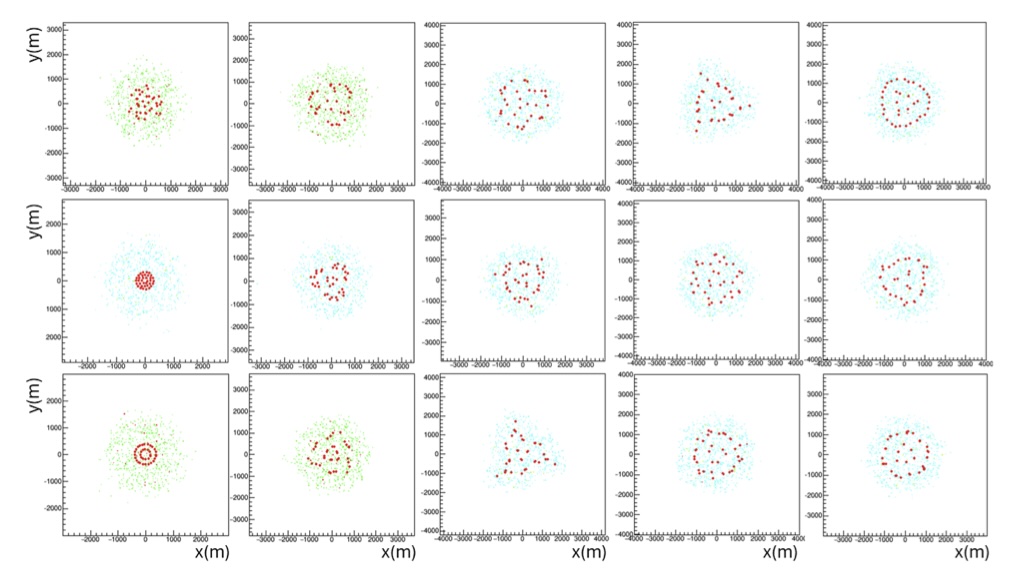
Tommaso Dorigo, et al.:
We present a continuous model of secondary particles from atmospheric showers and develop an optimization pipeline using stochastic gradient descent to identify the optimal layout for the SWGO water Cherenkov detector array. This approach aligns the detector configuration with the scientific goals of the experiment, demonstrating the capability to find global maxima in high-dimensional parameter spaces.
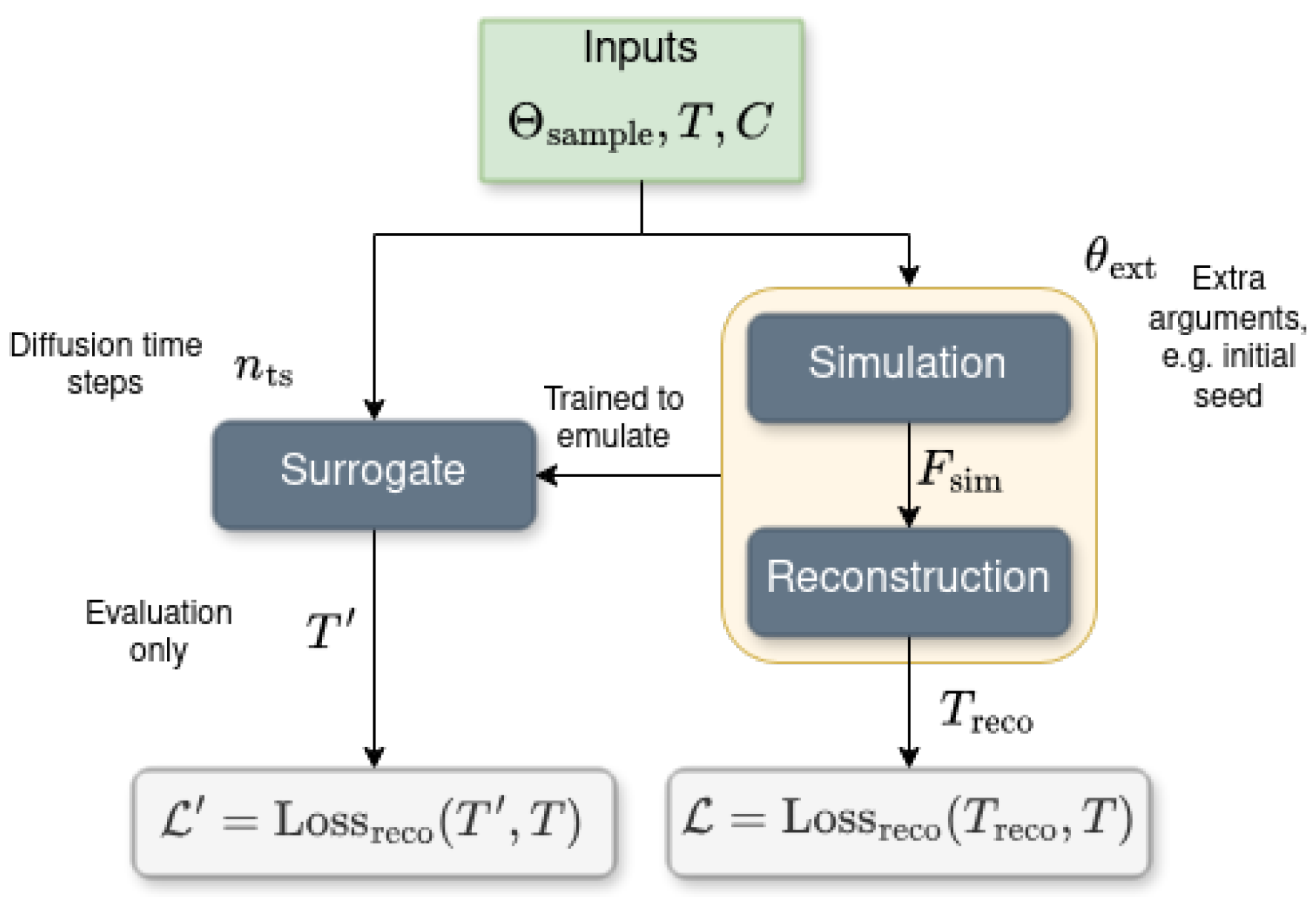
Kylian Schmidt, et al.:
We introduce AIDO, a framework using diffusion models for optimizing particle detectors. A case study on sampling calorimeters shows how end-to-end optimization across simulation and reconstruction can guide detector design using learned surrogates.
Tommaso Dorigo, et al.:
We explore how the design of fundamental science experiments can be guided by a utility function, balancing multiple objectives to optimize scientific outcomes.
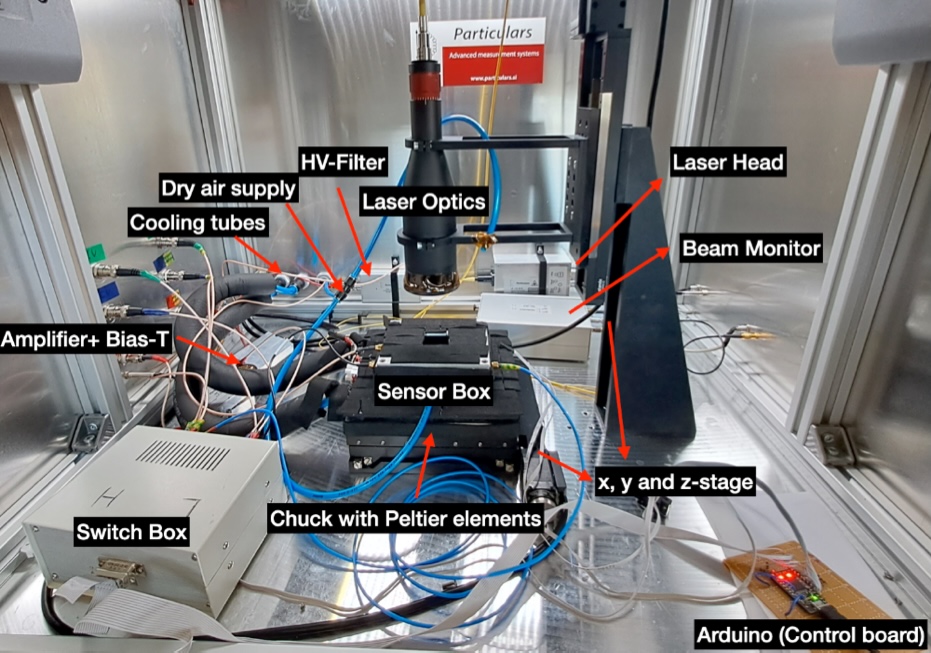
Oliwia Kałuzińska, et al.:
We investigate the annealing effects on charge collection in neutron-irradiated silicon diodes fabricated from 8-inch p-type wafers, providing insights for optimizing the layout of silicon modules in the High-Granularity Calorimeter (HGCAL) for the High-Luminosity LHC.
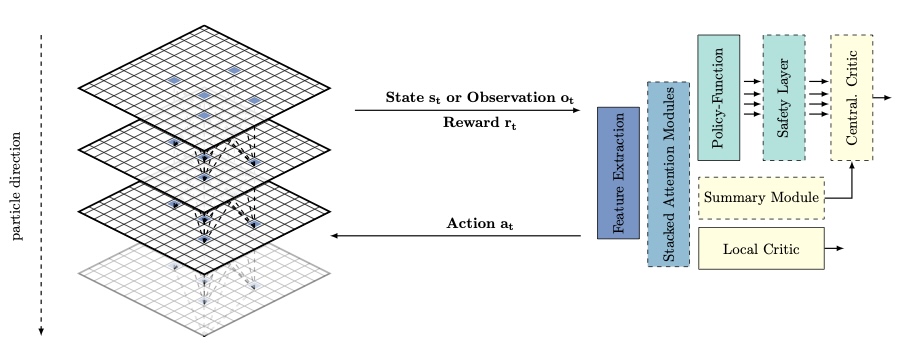
Tobias Kortus, et al.:
We introduce a multi-agent reinforcement learning approach with assignment constraints for reconstructing particle tracks in pixelated detectors. Our method collaboratively optimizes a policy to minimize particle scattering, employing a safety layer to ensure unique hit assignments and incorporating cost margins to enhance generalization. Empirical results on simulated proton imaging data demonstrate improved performance over existing single- and multi-agent baselines.
 Jan Kieseler is an experimental particle physicist working at the interface of fundamental research and advanced technologies. His work focuses on top quark and Higgs boson interactions, detector optimization, and machine learning in reconstruction and computing. At KIT, he teaches courses in modern particle physics and data analysis, and supervises Bachelor, Master, and PhD students on topics ranging from collider physics to AI-driven detector design.
Jan Kieseler is an experimental particle physicist working at the interface of fundamental research and advanced technologies. His work focuses on top quark and Higgs boson interactions, detector optimization, and machine learning in reconstruction and computing. At KIT, he teaches courses in modern particle physics and data analysis, and supervises Bachelor, Master, and PhD students on topics ranging from collider physics to AI-driven detector design.







