API Documentation
This page contains documentation which was automatically extracted from docstrings attached to the kafe2 source code. All major classes, methods and functions provided by kafe2 are documented here. For further information, or if in doubt about the exact functionality, users are invited to consult the source code itself. If you notice a mistake in the kafe2 documentation, or if you think that a particular part needs to be better documented, please open an issue on the kafe2 GitHub page.
kafe2 Wrappers
The easiest way to use kafe2 (as part of a Python program) is to use the wrapper functions below. These functions provide pre-configured pipelines for the most common use cases and do not require the user to manually manage objects.
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.custom_fit(cost_function, p0=None, dp0=None, limits=None, fixed=None, constraints=None, report=False, profile=True, save=True)
Built-in function for directly minimizing a cost function without any explicit model, data, or errors.
- Parameters:
cost_function (Callable) – The cost function to be minimized as a native Python function.
p0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter values for the fit.
dp0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter step size for the fit.
limits (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – limits to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each limit is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the lower bound, and then the upper bound. An iterable of limits can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
fixed (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – Model parameter to be fixed. The expected format for each parameter is the parameter name followed by an optional value to which the parameter should be set prior to fixing. An iterable of (name, value) tuples can be passed to fix multiple parameters.
constraints (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – constraints to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each constraint is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the parameter mean, and then the parameter uncertainty. An iterable of constraints can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
report (bool) – whether a report of the data and fit results should be printed to the console.
profile (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors and profile/contour plots.
save (bool) – whether the fit results should be saved to disk under results.
- Returns:
the fit results.
- Return type:
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.hist_fit(model_function=None, data=None, n_bins=None, bin_range=None, bin_edges=None, p0=None, dp0=None, error=None, error_rel=None, error_cor=None, error_cor_rel=None, errors_rel_to_model=True, density=True, gauss_approximation=None, limits=None, fixed=None, constraints=None, report=False, profile=True, save=True)
Built-in function for fitting a (probability density) function to one-dimensional data by binning the data. The uncertainty on the bins is assumed to follow a Poisson distribution. If any errors are specified then the Poisson distribution is instead approximated by a Gaussian distribution.
- Parameters:
model_function (Callable) – The model function as a native Python function where the first argument denotes the independent x variable. Alternatively an already defined
HistModelFunctionobject. Defaults to a normal distribution.data (typing.Sequence[float] or
kafe2.fit.hist.container.HistContainer) – the data for the fit. Can be either raw data, the result of np.histogram, or akafe2.fit.hist.container.HistContainerobject.n_bins (int) – how many bins raw data should be split into.
bin_range (Sequence[float] of length 2) – the lower and upper bound for the bins specified by n_bins.
bin_edges (Sequence[float]) – explicit bin edges for raw data. If
None, each bin will have the same width.p0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter values for the fit.
dp0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter step size for the fit.
error (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated absolute error on the bin heights.
error_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated relative error on the bin heights.
error_cor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated absolute error on the bin heights.
error_cor_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated relative error on the bin heights.
errors_rel_to_model (bool) – whether the relative y errors should be relative to the model. Otherwise they are relative to the data.
density (bool) – whether the model is a probability density function and the data should be normalized to match it.
limits (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – limits to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each limit is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the lower bound, and then the upper bound. An iterable of limits can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
fixed (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – Model parameter to be fixed. The expected format for each parameter is the parameter name followed by an optional value to which the parameter should be set prior to fixing. An iterable of (name, value) tuples can be passed to fix multiple parameters.
constraints (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – constraints to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each constraint is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the parameter mean, and then the parameter uncertainty. An iterable of constraints can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
report (bool) – whether a report of the data and fit results should be printed to the console.
profile (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors and profile/contour plots.
save (bool) – whether the fit results should be saved to disk under results.
- Returns:
the fit results.
- Return type:
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.indexed_fit(model_function=None, data=None, p0=None, dp0=None, error=None, error_rel=None, error_cor=None, error_cor_rel=None, errors_rel_to_model=True, limits=None, fixed=None, constraints=None, report=False, profile=True, save=True)
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.unbinned_fit(model_function=None, data=None, p0=None, dp0=None, limits=None, fixed=None, constraints=None, report=False, profile=True, save=True)
Built-in function for directly fitting a probability density function to one-dimensional data without binning the data.
- Parameters:
model_function (Callable) – The model function as a native Python function where the first argument denotes the independent x variable. Alternatively an already defined
ModelFunctionBaseobject. Defaults to a straight line.data (Sequence[float]) – the data values for the fit. Must be one-dimensional.
p0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter values for the fit.
dp0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter step size for the fit.
limits (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – limits to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each limit is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the lower bound, and then the upper bound. An iterable of limits can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
fixed (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – Model parameter to be fixed. The expected format for each parameter is the parameter name followed by an optional value to which the parameter should be set prior to fixing. An iterable of (name, value) tuples can be passed to fix multiple parameters.
constraints (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – constraints to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each constraint is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the parameter mean, and then the parameter uncertainty. An iterable of constraints can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
report (bool) – whether a report of the data and fit results should be printed to the console.
profile (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors and profile/contour plots.
save (bool) – whether the fit results should be saved to disk under results.
- Returns:
the fit results.
- Return type:
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.xy_fit(model_function=None, x_data=None, y_data=None, p0=None, dp0=None, x_error=None, y_error=None, x_error_rel=None, y_error_rel=None, x_error_cor=None, y_error_cor=None, x_error_cor_rel=None, y_error_cor_rel=None, errors_rel_to_model=True, limits=None, fixed=None, constraints=None, report=False, profile=None, save=True)
Built-in function for fitting a model function to xy data.
Interpretation of x_error, y_error, x_error_rel, and y_error_rel: If the input error is a simple float it is broadcast across the entire data vector. If the input error is a one-dimensional vector it is interpreted as a pointwise error vector. If the input error is a two-dimensional matrix it is interpreted as a covariance matrix.
Interpretation of x_error_cor, y_error_cor, x_error_cor_rel, and y_error_cor_rel: If the input error is a simple float it is broadcast across the entire data vector. If the input error is a one-dimensional vector then each individual value is added as a separate error that is being broadcast across the entire data vector.
- Parameters:
model_function (Callable) – The model function as a native Python function where the first argument denotes the independent x variable. Alternatively an already defined
ModelFunctionBaseobject. Defaults to a straight line.x_data (Sequence[float]) – the x data values for the fit. Must be one-dimensional.
y_data (Sequence[float]) – the y data values for the fit. Must be one-dimensional.
p0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter values for the fit.
dp0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter step size for the fit.
x_error (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated absolute x error.
y_error (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated absolute y error.
x_error_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated relative x error.
y_error_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated relative y error.
x_error_cor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated absolute x error.
y_error_cor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated absolute y error.
x_error_cor_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated relative x error.
y_error_cor_rel (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated relative y error.
errors_rel_to_model (bool) – whether the relative y errors should be relative to the model. Otherwise they are relative to the data.
limits (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – limits to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each limit is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the lower bound, and then the upper bound. An iterable of limits can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
fixed (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – Model parameter to be fixed. The expected format for each parameter is the parameter name followed by an optional value to which the parameter should be set prior to fixing. An iterable of (name, value) tuples can be passed to fix multiple parameters.
constraints (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – constraints to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each constraint is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the parameter mean, and then the parameter uncertainty. An iterable of constraints can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
report (bool) – whether a report of the data and fit results should be printed to the console.
profile (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors and profile/contour plots.
save (bool) – whether the fit results should be saved to disk under results.
- Returns:
the fit results.
- Return type:
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.plot(fits=-1, x_label=None, y_label=None, data_label=None, model_label=None, error_band_label=None, x_range=None, y_range=None, x_scale=None, y_scale=None, x_ticks=None, y_ticks=None, parameter_names=None, model_name=None, model_expression=None, font_scale=1.0, legend=True, fit_info=True, error_band=True, extra=None, profile=None, plot_profile=None, show=True, save=True)
Plots kafe2 fits.
- Parameters:
fits (int or
FitBaseor Sequence[FitBase]) – which kafe2 fits to use for the plot. A positive integer is interpreted as the fit with the given index that has been performed (with wrappers) since the program started. A negative integer -n is interpreted as the last n fits. kafe2 fit objects are used directly.x_label (str) – the x axis label.
y_label (str) – the y axis label.
data_label (str or Sequence[str]) – the data label(s) in the legend.
model_label (str or Sequence[str]) – the model label(s) in the legend (under data label).
error_band_label (str or Sequence[str]) – the error band label(s) in the legend.
x_range (Sequence[float], len(x_range) == 2) – x range for the plot.
y_range (Sequence[float], len(y_range) == 2) – y range for the plot.
x_scale ("linear" or "log") – the scale to use for the x axis.
y_scale ("linear" or "log") – the scale to use for the y axis.
x_ticks (Sequence[float]) – the ticks at which to show values on the x axis.
y_ticks (Sequence[float]) – the ticks at which to show values on the y axis.
parameter_names (dict) – custom parameter LaTeX names to display in the plot. The dictionary keys are the regular parameter names and the dictionary values are the names to show in the plot.
model_name (str or Sequence[str]) – the model LaTeX name(s) in the legend (in the mathematical expression of the model function).
model_expression (str or Sequence[str]) – the model LaTeX expression(s) in the legend.
legend (bool) – whether the legend should be shown.
fit_info (bool) – whether the fit information (fit results, goodness of fit) should be shown.
error_band ("ratio", "residual", or "pull".) – whether the model error band should be shown.
extra – additional, supplementary plots to show below the main plot.
profile (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors and profile/contour plots.
plot_profile (bool) – whether the profile plots should be created.
show (bool) – whether the plots should be shown.
save (bool) – whether the plots should be saved to disk under results.
font_scale (float) – multiply font size by this amount.
- Returns:
a kafe2 plot object containing the relevant matplotlib plots.
- Return type:
- kafe2.fit.util.wrapper.k2Fit(func, x, y, sx=None, sy=None, srelx=None, srely=None, xabscor=None, yabscor=None, xrelcor=None, yrelcor=None, ref_to_model=True, constraints=None, p0=None, dp0=None, limits=None, plot=True, axis_labels=['x-data', 'y-data'], data_legend='data', model_expression=None, model_name=None, model_legend='model', model_band='$\\pm 1 \\sigma$', fit_info=True, plot_band=True, asym_parerrs=True, plot_cor=False, showplots=True, quiet=True)
Legacy function for backwards compatibility with PhyPraKit. New code should not use this function. Fits a model to xy data and plots the results.
Interpretation of sx, sy, srelx, and srely: If the input error is a simple float it is broadcast across the entire data vector. If the input error is a one-dimensional vector it is interpreted as a pointwise error vector. If the input error is a two-dimensional matrix it is interpreted as a covariance matrix.
Interpretation of xabscor, yabscor, xrelcor, and yrelcor: If the input error is a simple float it is broadcast across the entire data vector. If the input error is a one-dimensional vector then each individual value is added as a separate error that is being broadcast across the entire data vector.
- Parameters:
func (Callable) – The model function as a native Python function where the first argument denotes the independent x variable. Alternatively an already defined
ModelFunctionBaseobject. Defaults to a straight line.x (Sequence[float]) – the x data values for the fit. Must be one-dimensional.
y (Sequence[float]) – the y data values for the fit. Must be one-dimensional.
sx (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated absolute x error.
sy (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated absolute y error.
srelx (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated relative x error.
srely (float or Sequence[float]) – uncorrelated relative y error.
xabscor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated absolute x error.
yabscor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated absolute y error.
xrelcor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated relative x error.
yrelcor (float or Sequence[float]) – correlated relative y error.
ref_to_model (bool) – whether the relative y errors should be relative to the model. Otherwise they are relative to the data.
constraints (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – constraints to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each constraint is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the parameter mean, and then the parameter uncertainty. An iterable of constraints can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
p0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter values for the fit.
dp0 (Sequence[float]) – the initial parameter step size for the fit.
limits (Sequence or Sequence[Union[list, tuple]]) – limits to be applied to the model parameter. The expected format for each limit is an iterable consisting of the parameter name, the lower bound, and then the upper bound. An iterable of limits can be passed to limit multiple parameters.
plot (bool) – whether the fit results should be plotted.
axis_labels (Sequence[str]) – the labels for the x and y axis.
data_legend (str) – the data label in the legend.
model_expression (str) – the model LaTeX expression in the legend.
model_name (str) – the model LaTeX name in the legend (in the mathematical expression of the model function).
model_legend (str) – the model label in the legend (under data label).
model_band (str) – the error band label in the legend.
fit_info (bool) – whether the fit information (fit results, goodness of fit) should be shown.
plot_band (bool) – whether the model error band should be shown.
asym_parerrs (bool) – whether the profile likelihood method should be used for asymmetric parameter errors.
plot_cor (bool) – whether the profile plots should be created.
showplots (bool) – whether the plots should be shown.
report (bool) – whether the report of the data and fit results should be suppressed.
- Returns:
a tuple containing the parameter values, the parameter errors, the parameter correlation matrix, and the minimal
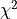 cost function value.
cost function value.- Return type:
kafe2 Object-Oriented Programming
Parameter Estimation Tools: fit
The kafe2.fit module provides an object-oriented toolkit for estimating model
parameters from data (“fitting”).
It distinguishes between a number of different data types:
xy data (dedicated submodule:
xy),series of indexed measurements (dedicated submodule:
indexed),histograms (dedicated submodule:
histogram),raw 1D data using the method of maximum likelihood (“unbinned fit”, dedicated submodule:
histogram), anddirect minimization of a cost function (dedicated submodule:
custom).
Each of the above data types has its own particularities when it comes to fitting. The main difference is due to the way uncertainties can be defined and interpreted for each type of data and how the fit results are presented.
XY Data
For xy data, one data set consists of a list of 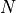 distinct
distinct 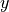 measurements
measurements
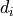 with the (discrete) index
with the (discrete) index 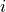 ranging from
ranging from 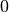 to
to 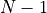 .
The measurements were taken at
.
The measurements were taken at 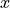 values
values 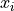 .
For each measurement in the series, one or more uncertainty sources can be defined,
each being a numerical estimate of how much the respective measurement has fluctuated from the
“true values”.
Correlations between uncertainties on separate measurements
.
For each measurement in the series, one or more uncertainty sources can be defined,
each being a numerical estimate of how much the respective measurement has fluctuated from the
“true values”.
Correlations between uncertainties on separate measurements 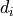 and
and 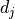 can also
be taken into account by using covariance/correlation matrices.
can also
be taken into account by using covariance/correlation matrices.
Additional uncertainites on 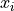 can also be defined.
When fitting an xy model to data they are converted to
can also be defined.
When fitting an xy model to data they are converted to 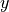 uncertainties via multiplication
with the derivative of the model function by
uncertainties via multiplication
with the derivative of the model function by 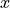 .
When plotting the result of xy fits, the model function is displayed as a continuous
function of
.
When plotting the result of xy fits, the model function is displayed as a continuous
function of 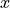 , and an error band can be computed to reflect the model uncertainty,
as determined by propagating the parameter uncertainties onto the y axis.
, and an error band can be computed to reflect the model uncertainty,
as determined by propagating the parameter uncertainties onto the y axis.
The following objects are provided for handling xy data:
XYContainer: data container for storing xy dataXYParametricModel: corresponding modelXYFit: a fit of a parametric model to xy data
Indexed data
Compared to xy data indexed data no longer has an explicit x axis. The data simply appears as an indexed list of data points. As a consequence the model function does not expect an independent variable.
The following objects are provided for handling indexed data, as described above:
IndexedContainer: data container for storing indexed dataIndexedParametricModel: corresponding modelIndexedFit: a fit of a parametric model to indexed data
Histograms
kafe2 is also able to handle histograms. Histograms organize measurements whose
values can fall anywhere across a continuum of values into a number of discrete regions
or “bins”. Typically, the continuous “measurement space” (a closed real interval
![[x_{\rm min}, x_{\rm max}]](../../_images/math/c9809eca2b8d4eda10847f0c117804f3b2ac3074.png) )
is subdivided into a sequence of successive intervals at the “bin edges”
)
is subdivided into a sequence of successive intervals at the “bin edges”
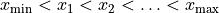 . Whenever a measurement falls into one of
the bins, the value of that histogram bin is incremented by one.
A histogram is completely defined by its bin edges and the bin values.
. Whenever a measurement falls into one of
the bins, the value of that histogram bin is incremented by one.
A histogram is completely defined by its bin edges and the bin values.
Note
The bin numbering starts at 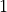 for the first bin and ends at
for the first bin and ends at 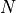 , where
, where 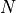 is defined as the size of the histogram. The bin numbers
is defined as the size of the histogram. The bin numbers  and
and 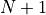 refer to
the underflow (below
refer to
the underflow (below  ) and overflow bin (above
) and overflow bin (above  ),
respectively.
),
respectively.
Defining a parametric model for histograms is not as straightforward as for xy and indexed data. Seeing as they keep track of the number of entries in different intervals of the continuum, the bin values can be interpreted using probability theory.
As the number of entries approaches infinity, the number of entries 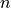 in the bin covering an
interval
in the bin covering an
interval 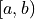 , divided by the total number of entries
, divided by the total number of entries 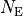 , will approach the
probablity of an event landing in that bin:
, will approach the
probablity of an event landing in that bin:
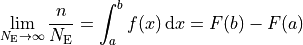
In the above formula, 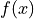 is the probability density function,
and
is the probability density function,
and 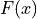 is an antiderivative of
is an antiderivative of 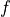 (for example the cumulative distribution function).
(for example the cumulative distribution function).
Using the above relation, the model prediction 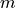 for the bin
for the bin 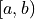 can be defined
as:
can be defined
as:
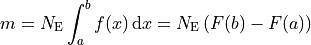
This means that, for histograms, the model density 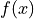 needs to be specified as the model
function.
The model is then calculated by numerically integrating this function over each bin.
needs to be specified as the model
function.
The model is then calculated by numerically integrating this function over each bin.
An alternative would be to specify the model density antiderviative 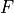 alongside
the model, so that the model can be calculated as a simple difference, rather than as an integral.
alongside
the model, so that the model can be calculated as a simple difference, rather than as an integral.
The following objects are provided for handling histograms:
HistContainer: data container for storing histogramsHistParametricModel: corresponding modelHistFit: a fit of a parametric model to histograms
Unbinned
If data is treated as unbinned the model function 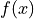 is interpreted as a
model density function.
The cost function value
is interpreted as a
model density function.
The cost function value 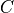 is then directly calculated as the negative log-likelihood of the
data given said PDF:
is then directly calculated as the negative log-likelihood of the
data given said PDF:
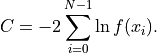
An unbinned fit is the edge case of a histogram fit for as the individual bins become infinitessimally thin.
The following objects are provided for handling unbinned data:
UnbinnedContainer: data container for storing unbinned dataUnbinnedParametricModel: corresponding modelUnbinnedFit: a fit of a parametric model to unbinned data
Custom
Lets the user directly define a cost function. Since this fit type does not have explicit data the fit results cannot be plotted automatically.
The following objects are provided for custom fits:
CustomFit: a fit for minimizing a cost function
Plots
For creating graphical representations of fits, the Plot is provided.
It can be instantiated with any fit object (or list of fit objects) as an argument and will produce
one or more plots accordingly using matplotlib.
- synopsis:
This module contains specialized objects for storing measurement data, defining and fitting parametric models to these data and producing graphical representations (“plots”) of the result. It relies on the
kafe2.coremodule for basic functionality.
Tools for Fitting xy Data: xy
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of ordered xy pairs. This fit type is used for most cases e.g. when performing fits for the first time or in physics laboratory courses.
- synopsis:
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of ordered xy pairs.
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYContainer(x_data, y_data, dtype=<class 'float'>)
Bases:
IndexedContainerThis object is a specialized data container for xy data.
Construct a container for xy data:
- Parameters:
- add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False)
Add an uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or Sequence[float]) – Pointwise uncertainties or a single uncertainty for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False)
Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_matrix (numpy.ndarray) – 2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the covariance or correlation matrixmatrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'.name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (Sequence[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties. This is mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given.
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- property data
2D array with shape
(2, size)containing a copy of the data stored in this container.- Return type:
- get_total_error(axis)
Get the error object representing the total uncertainty for a specific axis.
- property has_uncor_x_errors
Trueif at least one x uncertainty source, which is not fully correlated, is defined for the data container.- Return type:
- property has_x_errors
Trueif at least one x uncertainty source is defined for the data container.- Return type:
- property has_y_errors
Trueif at least one x uncertainty source is defined for the data container.- Return type:
- property x
1D array of length
[size]containing the x data.- Return type:
- property x_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the absolute data x correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property x_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the absolute data x covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property x_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the inverse of the absolute data x covariance matrix.Noneif singular.- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- property x_err
1D array containing the absolute total data x uncertainties.
- Return type:
- property y
1D array of length
sizecontaining the y data.- Return type:
- property y_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the absolute data y correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property y_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the absolute data y covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property y_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the inverse of absolute data y covariance matrix.Noneif singular.- Return type:
- property y_err
1D array of length
sizecontaining the absolute total data y uncertainties.- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, axes_to_use='xy', add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_Chi2Built-in least-squares cost function for xy data.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
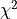 . This is either
‘covariance’`,
. This is either
‘covariance’`, 'pointwise'orNone.axes_to_use – The errors for the given axes are taken into account when calculating
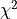 . Either
. Either 'y'or'xy'add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYCostFunction_GaussApproximation(errors_to_use='covariance', axes_to_use='xy', add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True)
Bases:
CostFunction_GaussApproximationBuilt-in Gaussian approximation of the Poisson negative log-likelihood cost function for xy data.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str) – Which errors to use when calculating
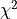 . This is either
‘covariance’`,
. This is either
‘covariance’`, 'pointwise'.axes_to_use – The errors for the given axes are taken into account when calculating
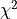 . Either
. Either 'y'or'xy'add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False, axes_to_use='xy')
Bases:
CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYFit(xy_data, model_function=<function linear_model>, cost_function='chi2', minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')
Bases:
FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to xy data.
- Parameters:
xy_data (XYContainer or Sequence) – A
XYContaineror a raw 2D array of shape(2, N)containing the measurement data.model_function (Callable) – The model function as a native Python function where the first argument denotes the independent x variable. Alternatively an already defined
XYModelFunctionobject. Defaults to a straight line.cost_function (str or Callable) – The cost function this fit uses to find the best parameters.
minimizer (str or None) – The minimizer to use for fitting. Either
None,"iminuit","tminuit", or"scipy".minimizer_kwargs (dict) – Dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
- CONTAINER_TYPE
alias of
XYContainer
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
ModelFunctionBase
- MODEL_TYPE
alias of
XYParametricModel
- PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE
alias of
XYPlotAdapter
- RESERVED_NODE_NAMES = {'cost', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cor_mat_inversex_data_cov_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error', 'x_cor_mat', 'x_cov_mat', 'x_cov_mat_inverse', 'x_error', 'y_data', 'y_data_cor_mat', 'y_data_cov_mat', 'y_data_cov_mat_inverse', 'y_data_error', 'y_model', 'y_model_cor_mat', 'y_model_cov_mat', 'y_model_cov_mat_inverse', 'y_model_error'}
- X_ERROR_ALGORITHMS = ('iterative linear', 'nonlinear')
- add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data')
Add an uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or Sequence[float]) – Pointwise uncertainties or a single uncertainty for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors. Either
'data'or'model'.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data')
Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_matrix (numpy.ndarray) – 2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the covariance or correlation matrixmatrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'.name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (Sequence[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties. This is mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given.
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors. Either
'data'or'model'.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- property data_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data xy correlation matrix projected onto the y axis.- Return type:
- property data_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis).- Return type:
- property data_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the data xy covariance matrix projected onto the y axis.Noneif singular.- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- property data_error
1D array containing the pointwise xy uncertainties projected onto the y axis.
- Return type:
- error_band(x=None)
Calculate the symmetric model uncertainty at every given point x. This is only possible after a fit has been performed with the
do_fitmethod.- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float]) – 1D array containing the values of x at which to calculate the model uncertainty.
- Returns:
1D array containing the model uncertainties at the given x values.
- Return type:
- eval_model_function(x=None, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float]) – 1D array containing the values of x at which to evaluate the model function. If
None, the data x valuesx_dataare used.model_parameters (Collection[float]) – The model parameter values. If
None, the current valuesparameter_valuesare used.
- Returns:
Model function values at the given x-values.
- Return type:
- eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(x=None, model_parameters=None, par_dx=None)
Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the model parameters.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float]) – 1D array containing the x values at which to evaluate the model function. If
None, the data x valuesx_dataare used.model_parameters (Collection[float]) – 1D array containing the model parameter values. If
None, the current valuesparameter_valuesare used.par_dx (Collection[float]) – 1D array with length
parscontaining the numeric differentiation step size for each parameter. IfNoneand a fit has been performed, 1% of the parameter uncertainties is used.
- Returns:
2D array of shape
(par, N)containing the model function derivatives for each parameter at the given x values.- Return type:
- property has_x_errors
True`if at least one x uncertainty source has been defined.- Return type:
- property has_y_errors
True`if at least one y uncertainty source has been defined- Return type:
- property model
2D array of shape
(2, N)containing the x and y model values- Return type:
- property model_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model xy correlation matrix projected onto the y axis.- Return type:
- property model_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model xy covariance matrix projected onto the y axis.- Return type:
- property model_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the model xy covariance matrix projected onto the y axis.None`if singular.- Return type:
- property model_error
1D array of pointwise model xy uncertainties projected onto the y axis.
- Return type:
- property total_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the total xy covariance matrix projected onto the y axis.- Return type:
- property total_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing theinverse of the total xy covariance matrix projected onto the y axis.Noneif singular.- Return type:
- property total_error
1D array of the total pointwise xy uncertainties projected onto the y axis.
- Return type:
- property x_data
1D array containing the measurement x values.
- Return type:
- property x_data_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data x correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property x_data_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data x covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property x_data_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the data x covariance matrix orNoneif singular.- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- property x_data_error
1D array containing the pointwise x data uncertainties
- Return type:
- property x_model
- .x_data for an
- Return type:
- Type:
1D array containing the model x values. The same as
- Type:
py;obj
- property x_model_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model x correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property x_model_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model x covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property x_model_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the model x covariance matrix orNoneif singular.- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- property x_model_error
1D array of pointwise model x uncertainties.
- Return type:
- property x_range
Minimum and maximum values of the x measurement data.
- property x_total_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the total x correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property x_total_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the total x covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property x_total_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing inverse of the total x covariance matrix.Noneif singular.- Return type:
- property x_total_error
1D array of total pointwise x uncertainties.
- Return type:
- property y_data
1D array containing the measurement y values.
- Return type:
- property y_data_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data y correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property y_data_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the data y covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property y_data_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the data y covariance matrix orNoneif singular.- Return type:
numpy.ndarray or None
- property y_data_error
1D array containing the pointwise y data uncertainties
- Return type:
- property y_model
1D array of y model predictions for the data points.
- Return type:
- property y_model_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model y correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property y_model_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the model y covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property y_model_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the inverse of the model y covariance matrix orNoneif singular.- Return type:
- property y_model_error
1D array of pointwise model y uncertainties.
- Return type:
- property y_range
Minimum and maximum values of the y measurement data.
- property y_total_cor_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the total y correlation matrix.- Return type:
- property y_total_cov_mat
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing the total y covariance matrix.- Return type:
- property y_total_cov_mat_inverse
2D array of shape
(N, N)containing inverse of the total y covariance matrix.Noneif singular.- Return type:
- property y_total_error
1D array of total pointwise y uncertainties
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYFitEnsemble(n_experiments, x_support, model_function, model_parameters, cost_function=<kafe2.fit.xy.cost.XYCostFunction_Chi2 object>, requested_results=None)
Bases:
FitEnsembleBaseObject for generating ensembles of fits to xy pseudo-data generated according to the specified uncertainty model.
After constructing an
XYFitEnsembleobject, an error model should be added to it. This is done as forXYFitobjects by using theadd_errororadd_matrix_errormethods.Once an uncertainty model is provided, the fit ensemble can be generated by using the
runmethod. This method starts by generating a pseudo-dataset in such a way that the empirical distribution of the data corresponds to the specified uncertainty model. It then fits the model to the pseudo-data and extracts information from the fit, such as the resulting parameter values or the value of the cost function at the minimum. This is repeated a large number of times in order to evaluate the whole ensemble in a statistically meaningful way.The ensemble result can be visualized by using the
plot_resultsmethod.Construct an
XYFitEnsembleobject.- Parameters:
n_experiments (int) – Number of pseudo experiments to perform.
x_support (Sequence[float]) – x values to use as support for calculating the “true” model (“true” x).
model_function (Callable) – The model function. Either a
XYModelFunctionobject or an unwrapped native Python function.model_parameters (Sequence[float]) – Parameters of the “true” model
cost_function (Callable) – The cost function used for the fits. Either a
CostFunctionBase-derived object or an unwrapped native Python function.requested_results (Sequence[str] or None.) – List of result variables to collect for each toy fit. If
Noneit will default to('y_pulls', 'parameter_pulls', 'cost').
- AVAILABLE_RESULTS = {'cost': <property object>, 'parameter_pulls': <property object>, 'x_data': <property object>, 'y_data': <property object>, 'y_model': <property object>, 'y_pulls': <property object>}
- AVAILABLE_STATISTICS = {'cor_mat': <property object>, 'cov_mat': <property object>, 'kurtosis': <property object>, 'mean': <property object>, 'mean_error': <property object>, 'skew': <property object>, 'std': <property object>}
- add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data')
Add an uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or Sequence[float]) – Pointwise uncertainties or a single uncertainty for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors. Either
'data'or'model'.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data')
Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_matrix (numpy.ndarray) – 2D array of shape
(size, size)containing the covariance or correlation matrixmatrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'.name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (Sequence[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties. This is mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given.
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors. Either
'data'or'model'.
- Returns:
An error id uniquely identifying the created error source.
- Return type:
- get_results(*results)
Return a dictionary containing the ensembles of result variables.
- get_results_statistics(results='all', statistics='all')
Return a dictionary containing statistics (e.g. mean) of the result variables.
- Parameters:
results (Iterable[str] or str) – Names of retrieved fit variable for which to return statistics. If
'all', get statistics for all retrieved variablesstatistics (Iterable[str] or str) – Names of statistics to retrieve for each result variable. If
'all', get all statistics for each retrieved variable
- Return type:
- plot_result_distributions(results='all', show_legend=True)
Make plots with histograms of the requested fit variable values across all pseudo-experiments.
- plot_result_scatter(results='all', show_legend=True)
Make scatter plots of the requested fit variable values across all pseudo-experiments.
- run()
Perform the pseudo-experiments. Retrieve and store the requested fit result variables.
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYParametricModel(x_data, model_func=<function linear_model>, model_parameters=(1.0, 1.0))
Bases:
ParametricModelBaseMixin,XYContainerConstruct an
XYParametricModelobject:- Parameters:
x_data (Collection[float]) – 1D array containing the x values supporting the model
model_func (Callable) – Python function handle of the model function.
model_parameters (Collection[float]) – 1D array containing the parameter values with which the model function should be initialized.
- property data
2D array with shape
(2, N)containing the model predictions.- Return type:
- eval_model_function(x=None, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float]) – 1D array containing the x values of the support points. If
None, the model x values are used.model_parameters (Collection[float] or None) – 1D array containing the values of the model parameters. If
None, the current values are used.
- Returns:
Values of the model function for the given parameters.
- Return type:
- eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(x=None, model_parameters=None, par_dx=None)
Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the model parameters.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float] or None) – 1D array with length
Ncontaining the x values of the support points. IfNone, the model x values are used.model_parameters (Collection[float] or None) – 1D array with length
parscontaining the values of the model parameters. IfNone, the current values are used.par_dx (Collection[float]) – 1D array with length
parscontaining the numeric differentiation step size for each parameter.
- Returns:
2D array with shape
(pars, N)containing the values of the model function derivatives with respect to the parameters.- Return type:
- eval_model_function_derivative_by_x(x=None, model_parameters=None, dx=None)
Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the independent variable.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray[float] or None) – 1D array containing the x values of the support points. If
None, the model x values are used.model_parameters (Collection[float] or None) – 1D array containing the values of the model parameters. If
None, the current values are used.dx (float or Collection[float]) – Step size for numeric differentiation.
- Returns:
1D array containing the values of the model function derivative for each parameter.
- Return type:
- property x
1D array containing the x support values.
- Return type:
- property y
1D array containing the y values calculated from the x support values and the current parameters.
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.xy.XYPlotAdapter(xy_fit_object, from_container=False)
Bases:
PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
XYPlotContainerfor aXYFitobject:- Parameters:
- AVAILABLE_X_SCALES = ('linear', 'log')
- PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE = 'xy'
- PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES = {'data': {'container_valid': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'hide': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_error_band': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_error_band', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_line': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_line', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'pull': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_pull', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'pull'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'ratio_error_band': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio_error_band', 'plot_style_as': 'model_error_band', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'residual': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'residual'}, 'residual_error_band': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual_error_band', 'plot_style_as': 'model_error_band', 'target_axes': 'residual'}}
- property model_line_y
y values of the model function at the support points
model_line_x.- Return type:
- property model_x
The x coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- property model_xerr
The magnitude of the model x error bars (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- property model_y
The y coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- property model_yerr
The magnitude of the model y error bars (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- plot_data(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model(target_axes, error_contributions=('model',), **kwargs)
Plot the model data to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str] Can either be
data,'model'or both.) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the model.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model_error_band(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot an error band around the model model function.
- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model_line(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the model function to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.plot.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_ratio_error_band(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot model error band around the data/model ratio to specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_residual_error_band(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot model error band around the data/model ratio to specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- update_plot_kwargs(plot_type, plot_kwargs)
Update the value of keyword arguments plot_kwargs to be passed to the plot method for for plot_type.
If a keyword argument should be removed, the value of the keyword in plot_kwargs can be set to the special value
'__del__'. To indicate that the default value should be used, the special value'__default__'can be set as a value.
- property x_scale
The x axis scale. Available scales are given in
AVAILABLE_X_SCALES- Return type:
- property y_error_band
1D array representing the uncertainty band around the model function at the support points
model_line_x.- Return type:
Tools for Fitting Series of Indexed Measurements: indexed
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of an indexed series of measurements. This can be useful for calculating weighted mean values or template fits.
- synopsis:
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of an indexed series of measurements.
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedContainer(data, dtype=<class 'float'>)
Bases:
DataContainerBaseThis object is a specialized data container for series of indexed measurements.
Construct a container for indexed data:
- Parameters:
data (iterable of type <dtype>) – a one-dimensional array of measurements
dtype (type) – data type of the measurements
- add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False)
Add an uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns:
error name
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False)
Add a matrix uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters:
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns:
error name
- Return type:
- property cor_mat
absolute data correlation matrix (
numpy.matrix)
- property cov_mat
absolute data covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix)
- property cov_mat_inverse
inverse of absolute data covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix), orNoneif singular
- property data
container data (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
- property data_range
the minimum and maximum value of the data
- Type:
return
- property err
absolute total data uncertainties (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
- property size
number of data points
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=False, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunctionConstruct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
cost_function (Callable) – function handle
arg_names (Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_Chi2Base class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
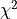 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate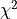 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction_GaussApproximation(errors_to_use='covariance', add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_GaussApproximationBase class for built-in Gaussian approximation of the Poisson negative log-likelihood cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str) – Which errors to use when calculating
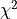 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'.add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedFit(data, model_function, cost_function='chi2', minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')
Bases:
FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to a series of indexed measurements.
- Parameters:
data (iterable of float) – the measurement values
model_function (
IndexedModelFunctionor unwrapped native Python function) – the model functioncost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionminimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
- CONTAINER_TYPE
alias of
IndexedContainer
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
IndexedModelFunction
- MODEL_TYPE
alias of
IndexedParametricModel
- PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE
alias of
IndexedPlotAdapter
- RESERVED_NODE_NAMES = {'cost', 'data', 'data_cor_mat', 'data_cov_mat', 'data_error', 'model', 'model_cor_mat', 'model_cov_mat', 'model_error', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error'}
- property model
array of model predictions for the data points
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedModelFunction(model_function)
Bases:
ModelFunctionBaseConstruct
IndexedModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
model_function – function handle
- FORMATTER_TYPE
alias of
IndexedModelFunctionFormatter
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedModelFunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, index_name='i', latex_index_name='i', arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)
Bases:
FunctionFormatterConstruct a
Formatterfor a model function for indexed data:- Parameters:
name – a plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name
latex_name – a LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name
index_name – a plain-text-formatted string representing the index
latex_index_name – a LaTeX-formatted string representing the index
arg_formatters – list of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function argumentsexpression_string – a plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression
latex_expression_string – a LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression
- get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)
Get a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters:
with_par_values – if
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f_i(a=1, b=2, ...))n_significant_digits (int) – number of significant digits for rounding
format_as_latex – if
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntaxwith_expression – if
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function
- Returns:
string
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedParametricModel(model_func, model_parameters, shape_like=None)
Bases:
ParametricModelBaseMixin,IndexedContainerConstruct an
IndexedParametricModelobject:- Parameters:
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
shape_like – array with the same shape as the model
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
IndexedModelFunction
- property data
model predictions (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
- property data_range
tuple containing the minimum and maximum of all model predictions
- eval_model_function(model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters:
model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)- Returns:
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type:
- eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(model_parameters=None, par_dx=None)
Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the model parameters.
- Parameters:
model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)par_dx (float) – step size for numeric differentiation
- Returns:
value(s) of the model function derivative for the given parameters
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedPlotAdapter(indexed_fit_object, from_container=False)
Bases:
PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
IndexedPlotContainerfor aIndexedFitobject:- Parameters:
fit_object – an
IndexedFitobjectfrom_container (bool) – Whether indexed_fit_object was created ad-hoc from just a data container.
- PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE = 'indexed'
- PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES = {'data': {'container_valid': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'hide': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'pull': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_pull', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'pull'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'residual': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'residual'}}
- property data_x
data x values
- property data_xerr
NoneforIndexedPlotContainer- Type:
x error bars for data
- property data_y
data y values
- property data_yerr
total uncertainty
- Type:
y error bars for data
- property model_x
model prediction x values
- property model_xerr
x error bars for model (actually used to represent the horizontal step length)
- property model_y
model prediction y values
- property model_yerr
NoneforIndexedPlotContainer- Type:
y error bars for model
- plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the model predictions to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
step_fill_betweenmethod
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
Tools for Fitting Histograms: histogram
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from histograms. Currently a histogram needs to be filled with all individual data points. A function for setting the bin heights is available but not recommended, as saving and loading those to and from a file is not yet supported.
- synopsis:
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from histograms.
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistContainer(n_bins=None, bin_range=None, bin_edges=None, fill_data=None, dtype=<class 'int'>)
Bases:
IndexedContainerThis object is a specialized data container for organizing data into histograms.
A histogram is a compact representation of a potentially large number of entries which are distributed along a continuum of values. Histograms divide the continuum into intervals (“bins”) and count the number of entries per interval.
Construct a histogram:
- Parameters:
n_bins (int) – how many bins raw data should be split into.
bin_range (iterable[float] of length 2) – the lower and upper bound for the bins specified by n_bins.
bin_edges (iterable[float]) – explicit bin edges for raw data. If
None, each bin will have the same width.fill_data (iterable[float]) – entries to fill into the histogram
dtype (type) – data type of histogram entries
- property bin_centers
a list of the (geometrical) bin centers
- property bin_edges
a list of the bin edges (including the outermost ones)
- property bin_range
a tuple containing the lower and upper edges of the histogram
- property bin_widths
a list of the bin widths
- property data
the number of entries in each bin
- fill(entries)
Fill new entries into the histogram.
- Parameters:
entries (list of floats) – list of entries
- property high
the upper edge of the histogram
- property low
the lower edge of the histogram
- property n_bins
the number of bins
- property n_entries
the number of entries
- property overflow
the number of entries in the overflow bin
- property raw_data
the number of entries in each bin
- rebin(new_bin_edges)
Change the histogram binning.
- set_bins(bin_heights, underflow=0, overflow=0)
Set the bin heights according to a pre-calculated histogram :param bin_heights: Heights of the bins :type bin_heights: list of int :param underflow: Number of entries in the underflow bin :type underflow: int :param overflow: Number of entries in the overflow bin :type overflow: int
- property size
the number of bins (excluding underflow and overflow bins)
- property underflow
the number of entries in the underflow bin
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=False, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunctionConstruct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
cost_function (Callable) – function handle
arg_names (Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_Chi2Base class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
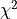 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate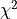 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction_GaussApproximation(errors_to_use='covariance', add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_GaussApproximationBase class for built-in Gaussian approximation of the Poisson negative log-likelihood cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str) – Which errors to use when calculating
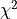 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'.add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)
Bases:
CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistFit(data, model_function=<function normal_distribution>, cost_function=<kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihood object>, bin_evaluation='simpson', density=True, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')
Bases:
FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to a histogram. If bin_evaluation is a Python function or of a numpy.vectorize object it is interpreted as the antiderivative of model_density_function. If bin_evaluation is equal to “rectangle”, “midpoint”, “trapezoid”, or “simpson” the bin heights are evaluated according to the corresponding quadrature formula. If bin_evaluation is equal to “numerical” the bin heights are evaluated by numerically integrating model_density_function.
- Parameters:
data (
HistContaineror two-dimensional iterable of bin heights and bin edges as returned by np.histogram.) – an encapsulated representation of the histogrammed data.model_function – the model (density) function
cost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionbin_evaluation (str, callable, or numpy.vectorize) – how the model evaluates bin heights.
density (bool) – if True, scale model function to the number of data points.
minimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
- CONTAINER_TYPE
alias of
HistContainer
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
HistModelFunction
- MODEL_TYPE
alias of
HistParametricModel
- PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE
alias of
HistPlotAdapter
- RESERVED_NODE_NAMES = {'cost', 'data', 'data_cor_mat', 'data_cov_mat', 'data_error', 'model', 'model_cor_mat', 'model_cov_mat', 'model_density', 'model_error', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error'}
- property density
- eval_model_function_density(x, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function density.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
model function density values
- Return type:
- property model
array of model predictions for the data points
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistModelFunction(model_function=None)
Bases:
ModelFunctionBaseConstruct
XYModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
model_function – function handle
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistParametricModel(n_bins, bin_range, model_density_func=<function normal_distribution>, model_parameters=[1.0, 1.0], bin_edges=None, bin_evaluation='simpson', density=True)
Bases:
ParametricModelBaseMixin,HistContainerMixin constructor: sets and initialized the model function.
- Parameters:
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
HistModelFunction
- property bin_evaluation
how the model evaluates bin heights. :rtype str, callable, or numpy.vectorize
- Type:
return
- property bin_evaluation_string
string representation of how the model evaluates bin heights. :rtype str
- Type:
return
- property data
model predictions (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
- property density
- eval_model_function_density(x, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function density.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.histogram.HistPlotAdapter(hist_fit_object, from_container=False)
Bases:
PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
HistPlotContainerfor aHistFitobject:- Parameters:
- AVAILABLE_X_SCALES = ('linear', 'log')
- PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE = 'histogram'
- PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES = {'data': {'container_valid': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'hide': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_density': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_density', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'pull': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_pull', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'pull'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'residual': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'residual'}}
- property data_x
data x values
- property data_xerr
x error bars for data (actually used to represent the bins)
- property data_y
data y values
- property data_yerr
total uncertainty
- Type:
y error bars for data
- property model_density_x
x support points for model density plot
- property model_density_y
value of model density at the support points
- property model_x
model prediction x values
- property model_xerr
x error bars for model (actually used to represent the bins)
- property model_y
model prediction y values
- property model_yerr
NoneforHistPlotContainer- Type:
y error bars for model
- plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethoderrorbar
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the model predictions to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodbar
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model_density(target_axes, **kwargs)
Plot the model density to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodplot
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
Tools for Unbinned Fits: unbinned
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from unbinned datasets. Those fits are used when there are two few data points to fill a histogram. Unbinned fits are essentially the ground truth for histogram fits as there is no modification of the data points through the binning. As each data point is considered, performing an unbinned fit can take much longer than a histogram fit, where each bin is considered.
- synopsis:
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from unbinned datasets.
- class kafe2.fit.unbinned.UnbinnedContainer(data, dtype=<class 'float'>)
Bases:
IndexedContainerThis object is a specialized data container for series of measurements.
Construct a container for indexed data:
- Parameters:
data (iterable of type <dtype>) – a one-dimensional array of measurements
dtype (type) – data type of the measurements
- add_error()
Add an uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns:
error name
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error()
Add a matrix uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters:
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns:
error name
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit.unbinned.UnbinnedCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood
Bases:
CostFunctionBuilt-in negative log-likelihood cost function for Unbinned data.
When using an unbinned dataset, the negative log-likelihood is the best method to fit a probability density funtion pdf to the density of the datapoints
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
- static nll(model)
- class kafe2.fit.unbinned.UnbinnedFit(data, model_function='normal_distribution', cost_function=<kafe2.fit.unbinned.cost.UnbinnedCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood object>, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None)
Bases:
FitBaseConstruct a fit to a model of unbinned data.
- Parameters:
data – the data points
model_function (
ModelFunctionBaseor unwrapped native Python function) – the model densitycost_function – the cost function
minimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
- CONTAINER_TYPE
alias of
UnbinnedContainer
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
ModelFunctionBase
- MODEL_TYPE
alias of
UnbinnedParametricModel
- PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE
alias of
UnbinnedPlotAdapter
- RESERVED_NODE_NAMES = {'cost', 'data', 'model', 'parameter_constraints', 'parameter_values'}
- property data_range
The minimum and maximum value of the data
- eval_model_function(x=None, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
model function values
- Return type:
- property goodness_of_fit
- property model
array of model predictions for the data points
- report(output_stream=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>, asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)
Print a summary of the fit state and/or results.
- Parameters:
output_stream (io.TextIOBase) – The output stream to which the report should be printed.
show_data (bool) – If
True, print out information about the data.show_model (bool) – If
True, print out information about the parametric model.show_fit_results (bool) – If
True, print out information about the fit results.asymmetric_parameter_errors (bool) – If
True, use two different parameter errors for up/down directions.
- class kafe2.fit.unbinned.UnbinnedParametricModel(data, model_density_function=<function normal_distribution>, model_parameters=[1.0, 1.0])
Bases:
ParametricModelBaseMixin,UnbinnedContainerMixin constructor: sets and initialized the model function.
- Parameters:
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
- property data
container data (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
- eval_model_function(support=None, model_parameters=None)
Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters:
support (list or
None) – x values of the support points (ifNone, the model support values are used)model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)
- Returns:
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type:
- property support
- class kafe2.fit.unbinned.UnbinnedPlotAdapter(unbinned_fit_object, from_container=False)
Bases:
PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
UnbinnedPlotAdapterfor aUnbinnedFitobject:- Parameters:
unbinned_fit_object – an
UnbinnedFitobjectfrom_container (bool) – Whether unbinned_fit_object was created ad-hoc from just a data container.
- AVAILABLE_X_SCALES = ('linear', 'log')
- PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE = 'unbinned'
- PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES = {'data': {'container_valid': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'hide': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_line': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_line', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'pull': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_pull', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'pull'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'residual': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'residual'}}
- property model_line_x
x support values for model function
- property model_line_y
The ‘y’ coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Returns:
iterable
- property model_x
x support values for model function
- property model_xerr
The magnitude of the model ‘x’ error bars (used by
plot_model).- Returns:
iterable
- property model_y
The ‘y’ coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Returns:
iterable
- property model_yerr
The magnitude of the model ‘y’ error bars (used by
plot_model).- Returns:
iterable
- plot_data(target_axes, height=None, **kwargs)
Method called by the main plot routine to plot the data points to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectheight (float) – The height of the lines which represent the density
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)
Method called by the main plot routine to plot the model to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
step_fill_betweenmethod
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_model_line(target_axes, **kwargs)
Method called by the main plot routine to plot the model to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
step_fill_betweenmethod
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_ratio(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_residual(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the residuals to a
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
Abstract Base Classes: _base
- synopsis:
This submodule contains the abstract base classes for all objects used by the
kafe2.fitmodule.
- class kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=False, fast_math=False)
Bases:
FileIOMixin,objectBase class for cost functions. Built from a Python function with some extra functionality used by Fit objects.
Any Python function returning a
floatcan be used as a cost function, although a number of common cost functions are provided as built-ins for all fit types.In order to be used as a model function, a native Python function must be wrapped by an object whose class derives from this base class. There is a dedicated
CostFunctionspecialization for each type of fit.This class provides the basic functionality used by all
CostFunctionobjects. These use introspection (inspect) for determining the parameter structure of the cost function and to ensure the function can be used as a cost function (validation).Construct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
cost_function (Callable) – function handle
arg_names (Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- property add_determinant_cost
Whether the determinant cost is being added automatically to the cost function value.
- property arg_names
The names of the cost function arguments.
- property argument_formatters
The
Formatterobjects for the function arguments
- chi2_probability(cost_function_value, ndf)
The chi2 probability associated with this cost function, None for non-chi2 cost functions.
- property errors_valid
- property fast_math
Prefer speed over numerical stability.
- property formatter
The
Formatterobject for this function
- property func
The cost function handle
- get_uncertainty_gaussian_approximation(data)
Get the gaussian approximation of the uncertainty inherent to the cost function, returns 0 by default.
- Parameters:
data – the fit data
- Returns:
the approximated gaussian uncertainty given the fit data
- goodness_of_fit(*args)
How well the model agrees with the data.
- property is_chi2
Whether the cost function is a chi2 cost function.
- is_data_compatible(data)
Tests if model data is compatible with cost function
- Parameters:
data (numpy.ndarray) – the fit data
- Returns:
if the data is compatible, and if not a reason for the incompatibility
- Return type:
(boo, str)
- property kafe2go_identifier
Short string representation (if any) of this cost function when dumping to file.
- property name
The cost function name (a valid Python identifier)
- property needs_errors
Whether the cost function needs errors for a meaningful result
- property pointwise
True if cost function result does not depend on covariances.
- property pointwise_version
Optimized version of cost function that uses pointwise errors, can be None.
- property saturated
Whether the cost function value is calculated from a saturated likelihood.
- class kafe2.fit._base.CostFunctionFormatter(name, name_saturated=None, latex_name=None, latex_name_saturated=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)
Bases:
FunctionFormatterA Formatter class for Cost Functions.
Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters:
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
- get_formatted(value=None, n_degrees_of_freedom=None, with_name=True, saturated=False, with_value_per_ndf=True, format_as_latex=False)
Get a formatted string representing this cost function.
- Parameters:
value (float or None) – Value of the cost function (if not
None, the returned string will include this).n_degrees_of_freedom (int or None) – Number of degrees of freedom (if not
None, the returned string will include this).with_name (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the cost function namesaturated (bool) – If
True, the cost function name for the saturated Likelihood will be used (no effect for chi2).with_value_per_ndf (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the value-ndf ratio as a decimal valueformat_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax
- Return type:
- property latex_name_saturated
A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the saturated function name.
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunctionBase class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
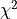 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate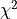 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- chi2_covariance(data, model, total_cov_mat_qr)
A least-squares cost function calculated from (y) data and model values, considering the covariance matrix of the (y) measurements. The cost function value can be calculated as follows:
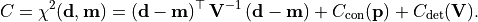
In the above,
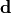 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
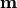 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
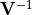 is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
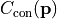 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and 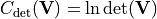 is the additional cost to compensate
for a non-constant covariance matrix.
is the additional cost to compensate
for a non-constant covariance matrix.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
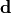
model – model predictions
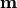
total_cov_mat_qr – QR decomposition of the total covariance matrix
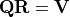
- Returns:
cost function value
- chi2_covariance_fast(data, model, total_cov_mat_cholesky)
Same as
chi2_covariancebut faster at the cost of numerical stability.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
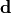
model – model predictions
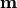
total_cov_mat_cholesky – Cholesky decomposition of the total covariance matrix
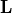 with
with 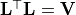
- Returns:
cost function value
- chi2_no_errors(data, model)
A least-squares cost function calculated from (y) data and model values, without considering uncertainties:
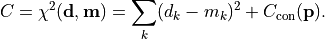
In the above,
 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
 are the model predictions,
and
are the model predictions,
and  is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
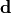
model – model predictions
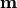
- Returns:
cost function value
- chi2_pointwise_errors(data, model, total_error)
A least-squares cost function calculated from (y) data and model values, considering pointwise (uncorrelated) uncertainties for each data point:
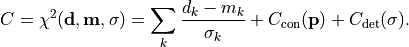
In the above,
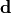 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
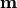 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
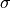 are the pointwise total uncertainties,
are the pointwise total uncertainties,
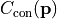 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and 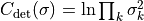 is the additional cost
to compensate for non-constant errors.
is the additional cost
to compensate for non-constant errors.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
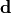
model – model predictions
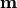
total_error – total error vector
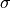
- Returns:
cost function value
- property pointwise
True if cost function result does not depend on covariances.
- property pointwise_version
Optimized version of cost function that uses pointwise errors, can be None.
- class kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction_GaussApproximation(errors_to_use='covariance', add_constraint_cost=True, add_determinant_cost=True, fast_math=False)
Bases:
CostFunctionBase class for built-in Gaussian approximation of the Poisson negative log-likelihood cost function.
- Parameters:
errors_to_use (str) – Which errors to use when calculating
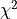 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'.add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.add_determinant_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically increase the cost function value by the logarithm of the determinant of the covariance matrix to reduce bias.fast_math (bool) – If
True, prefer speed over numerical stability.
- gaussian_approximation_covariance(data, model, total_cov_mat)
A least-squares cost function calculated from (y) data and model values, considering the covariance matrix of the (y) measurements. The cost function value can be calculated as follows:
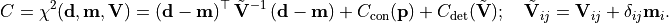
In the above,
 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
 is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
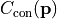 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters,
and 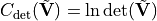 is the additional cost to
compensate for a non-constant covariance matrix.
is the additional cost to
compensate for a non-constant covariance matrix.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
model – model predictions
total_cov_mat – The total covariance matrix
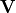
- Returns:
cost function value
- gaussian_approximation_pointwise_errors(data, model, total_error)
A least-squares cost function calculated from data and model values, considering pointwise (uncorrelated) uncertainties for each data point:
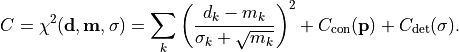
In the above,
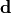 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
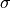 are the pointwise total uncertainties,
are the pointwise total uncertainties,
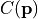 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters,
and
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters,
and 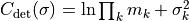 is the additional cost
to compensate for non-constant errors.
is the additional cost
to compensate for non-constant errors.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
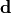
model – model predictions
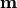
total_error – total error vector
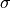
- Returns:
cost function value
- get_uncertainty_gaussian_approximation(data)
Get the gaussian approximation of the uncertainty inherent to the cost function, returns 0 by default.
- Parameters:
data – the fit data
- Returns:
the approximated gaussian uncertainty given the fit data
- goodness_of_fit(*args)
How well the model agrees with the data.
- property pointwise
True if cost function result does not depend on covariances.
- property pointwise_version
Optimized version of cost function that uses pointwise errors, can be None.
- class kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)
Bases:
CostFunctionBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
- Parameters:
- get_uncertainty_gaussian_approximation(data)
Get the gaussian approximation of the uncertainty inherent to the cost function, returns 0 by default.
- Parameters:
data – the fit data
- Returns:
the approximated gaussian uncertainty given the fit data
- is_data_compatible(data)
Tests if model data is compatible with cost function
- Parameters:
data (numpy.ndarray) – the fit data
- Returns:
if the data is compatible, and if not a reason for the incompatibility
- Return type:
(boo, str)
- static nll_gaussian(data, model, total_error)
A negative log-likelihood function assuming Gaussian statistics for each measurement.
The cost function is given by:

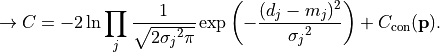
In the above,
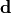 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
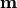 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
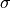 are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and
are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and 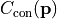 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
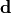
model – model predictions
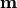
total_error – total error vector
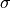
- Returns:
cost function value
- static nll_poisson(data, model)
A negative log-likelihood function assuming Poisson statistics for each measurement.
The cost function is given by:
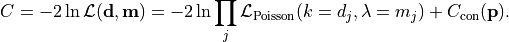
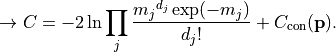
In the above,
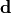 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
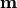 are the model predictions,
and
are the model predictions,
and 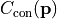 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained
parameters.- Parameters:
data – measurement data
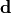
model – model predictions
- Returns:
cost function value
- static nllr_gaussian(data, model, total_error)
- static nllr_poisson(data, model)
- class kafe2.fit._base.DataContainerBase
Bases:
FileIOMixinThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of data containers.
It stores measurement data and uncertainties.
- add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference=None)
Add an uncertainty source to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or numpy.ndarray[float]) – Pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (Iterable[float] or None) – The data values to use when computing absolute errors from relative ones (and vice-versa)
- Returns:
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference=None)
Add a matrix uncertainty source to the data container.
- Parameters:
err_matrix – Covariance or correlation matrix.
matrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'.name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If :py:obj`None`, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.
err_val (Iterable[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given).
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (Iterable[float] or None) – the data values to use when computing absolute errors from relative ones (and vice-versa)
- Returns:
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type:
- property axis_labels
The axis labels describing the dataset.
- abstract property cov_mat
A numpy matrix containing the covariance matrix of the data.
- Return type:
- abstract property cov_mat_inverse
obj`None` if not invertible).
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray[numpy.ndarray[float]] or None
- Type:
A numpy matrix containing inverse of the data covariance matrix (or
- Type:
py
- abstract property data
A numpy array containing the data values.
- Return type:
- disable_error(error_name)
Temporarily disable an uncertainty source so that it doesn’t count towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters:
error_name (str) – error name
- enable_error(error_name)
(Re-)Enable an uncertainty source so that it counts towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters:
error_name (str) – error name
- abstract property err
A numpy array containing the pointwise data uncertainties.
- Return type:
- get_error(error_name)
Return the uncertainty object holding the uncertainty.
Note
If you modify this object, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be forced by calling
enable_error.- Parameters:
error_name (str) – error name
- Returns:
error object
- Return type:
kafe2.core.error.GaussianErrorBase
- get_matching_errors(matching_criteria=None, matching_type='equal')
Return a list of uncertainty objects fulfilling the specified matching criteria.
- Valid keys for matching_criteria:
name(the unique error name)type(eithersimpleormatrix)correlated(bool, only matches simple errors!)relative(bool)
Note
The error objects contained in the dictionary are not copies, but the original error objects. Modifying them is possible, but not recommended. If you do modify any of them, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be done by calling the private method
_clear_total_error_cache.- Parameters:
matching_criteria (dict or None) – Key-value pairs specifying matching criteria. The resulting error array will only contain error objects matching all provided criteria. If
None, all error objects are returned.matching_type (str) – How to perform the matching. If
'equal', the value in matching_criteria is checked for equality against the stored value. If'regex', the value in matching_criteria is interpreted as a regular expression and is matched against the stored value.
- Returns:
Dict mapping error name to
GaussianErrorBase-derived error objects.- Return type:
- get_total_error()
Get the error object representing the total uncertainty.
- Returns:
error object representing the total uncertainty
- Return type:
kafe2.core.error.MatrixGaussianError
- class kafe2.fit._base.FitBase(data, model_function, cost_function, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')
Bases:
FileIOMixin,objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fitters.
This is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fits.
- Parameters:
- CONTAINER_TYPE
alias of
DataContainerBase
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE = None
- MODEL_TYPE = None
- PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE = None
- RESERVED_NODE_NAMES = {}
- add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data', **kwargs)
Add an uncertainty source to the fit.
- Parameters:
err_val (float or Iterable[float]) – Pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Either
'data'or'model'. Specifies which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors.
- Returns:
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data', **kwargs)
Add a matrix uncertainty source for use in the fit.
- Parameters:
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (Iterable[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given).
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Either
'data'or'model'. Specifies which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors.
- Returns:
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type:
- add_matrix_parameter_constraint(names, values, matrix, matrix_type='cov', uncertainties=None, relative=False)
Advanced class for applying correlated constraints to several parameters of a fit. The order of names, values, matrix, and uncertainties must be aligned. In other words the first index must belong to the first value, the first row/column in the matrix, etc.
Let N be the number of parameters to be constrained.
- Parameters:
names (Collection[str]) – The names of the parameters to be constrained. Must be of shape (N,).
values (Sized[float]) – The values to which the parameters should be constrained. Must be of shape shape (N,).
matrix (Iterable[float]) – The matrix that defines the correlation between the parameters. By default interpreted as a covariance matrix. Can also be interpreted as a correlation matrix by setting matrix_type. Must be of shape shape (N, N).
matrix_type (str) – Either
'cov'or'cor'. Defines whether the matrix should be interpreted as a covariance matrix or as a correlation matrix.uncertainties (None or Iterable[float]) – The uncertainties to be used in conjunction with a correlation matrix. Must be of shape (N,)
relative (bool) – Whether the covariance matrix/the uncertainties should be interpreted as relative to values.
- add_parameter_constraint(name, value, uncertainty, relative=False)
Apply a simple gaussian constraint to a single fit parameter.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the parameter to be constrained.
value (float) – The value to which the parameter should be constrained.
uncertainty (float) – The uncertainty with which the parameter should be constrained to the given value.
relative (bool) – Whether the given uncertainty is relative to the given value.
- assign_model_function_expression(expression_format_string)
Assign a plain-text-formatted expression string to the model function.
- Parameters:
expression_format_string (str) – The plain text string.
- assign_model_function_latex_expression(latex_expression_format_string)
Assign a LaTeX-formatted expression string to the model function.
- Parameters:
latex_expression_format_string (str) – The LaTeX string. Elements like
'{par_name}'will be replaced automatically with the corresponding LaTeX names for the given parameter. These can be set withassign_parameter_latex_names.
- assign_model_function_latex_name(latex_name)
Assign a LaTeX-formatted string to be the model function name.
- Parameters:
latex_name (str) – The LaTeX string.
- assign_model_function_name(name)
Assign a string to be the model function name.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The new name.
- assign_parameter_latex_names(**par_latex_names_dict)
Assign LaTeX-formatted strings to all model function arguments.
- Parameters:
par_latex_names_dict – Dictionary mapping the parameter names to their latex names.
- assign_parameter_names(**par_names_dict)
Assign display strings to all model function arguments.
- Parameters:
par_names_dict – Dictionary mapping the parameter names to their display names.
- property asymmetric_parameter_errors
The current asymmetric parameter uncertainties.
- Return type:
- property chi2_probability
The chi2 probability for the current model values.
- property data
array of measurement values
- property data_container
The data container used in this fit.
- Return type:
- property data_cor_mat
the data correlation matrix
- property data_cov_mat
the data covariance matrix
- property data_cov_mat_inverse
inverse of the data covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
- property data_error
array of pointwise data uncertainties
- disable_error(err_id)
Temporarily disable an uncertainty source so that it doesn’t count towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters:
err_id (str) – error id
- do_fit(asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)
Perform the minimization of the cost function.
- property dynamic_error_algorithm
The algorithm to use for handling errors that depend on the model parameters. :rtype: str
- enable_error(err_id)
(Re-)Enable an uncertainty source so that it counts towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters:
err_id (str) – error id
- property errors_valid
- fix_parameter(name, value=None)
Fix a parameter so that its value doesn’t change when calling
do_fit.- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the parameter to be fixed
value (float or None) – The value to be given to the fixed parameter. If
Nonethe current value fromparameter_valueswill be used.
- get_matching_errors(matching_criteria=None, matching_type='equal')
Return a list of uncertainty objects fulfilling the specified matching criteria.
- Valid keys for matching_criteria:
name(the unique error name)type(either'simple'or'matrix')correlated(bool, only matches simple errors!)reference(either'model'or'data')
Note
The error objects contained in the dictionary are not copies, but the original error objects. Modifying them is possible, but not recommended. If you do modify any of them, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be done by calling the private dataset method
_clear_total_error_cache.- Parameters:
matching_criteria (dict or None) – Key-value pairs specifying matching criteria. The resulting error array will only contain error objects matching all provided criteria. If
None, all error objects are returned.matching_type (str) – How to perform the matching. If
'equal', the value in matching_criteria is checked for equality against the stored value. If'regex', the value in matching_criteria is interpreted as a regular expression and is matched against the stored value.
- Returns:
Dict mapping error name to
GaussianErrorBase-derived error objects.- Return type:
- get_result_dict(asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)
Return a dictionary of the fit results.
- property goodness_of_fit
- property has_data_errors
Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for the data.- Return type:
- property has_errors
Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for either the data or the model.- Return type:
- property has_model_errors
Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for the model.- Return type:
- limit_parameter(name, lower=None, upper=None)
Limit a parameter to a given range.
- load_state(filename: str, file_format: str | None = None)
load current fit state from the specified file that was written with save_state.
- abstract property model
- property model_cor_mat
the model correlation matrix
- property model_count
The number of model functions contained in the fit, 1 by default.
- Return type:
- property model_cov_mat
the model covariance matrix
- property model_cov_mat_inverse
inverse of the model covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
- property model_error
array of pointwise model uncertainties
- property model_function
The wrapped model function as a
ModelFunctionBaseor derived object. This object contains the model function as well as formatting information used for this fit.- Return type:
- property parameter_constraints
The gaussian constraints given for the fit parameters.
- Return type:
list[kafe2.core.constraint.GaussianSimpleParameterConstraint or kafe2.core.constraint.GaussianMatrixParameterConstraint]
- property parameter_cor_mat
The current parameter correlation matrix.
- Return type:
None or numpy.ndarray[numpy.ndarray[float]]
- property parameter_cov_mat
The current parameter covariance matrix.
- Return type:
None or numpy.ndarray[numpy.ndarray[float]]
- property parameter_errors
The current parameter uncertainties. Can be set to control initial step size during minimization.
- Return type:
- property parameter_name_value_dict
A dictionary mapping each parameter name to its current value.
- property parameter_values
The current parameter values.
- Return type:
- release_parameter(name)
Release a fixed parameter so that its value once again changes when calling
do_fit.- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the fixed parameter to be released
- report(output_stream=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>, show_data=True, show_model=True, show_fit_results=True, asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)
Print a summary of the fit state and/or results.
- Parameters:
output_stream (io.TextIOBase) – The output stream to which the report should be printed.
show_data (bool) – If
True, print out information about the data.show_model (bool) – If
True, print out information about the parametric model.show_fit_results (bool) – If
True, print out information about the fit results.asymmetric_parameter_errors (bool) – If
True, use two different parameter errors for up/down directions.
- save_state(filename: str, file_format: str | None = None, calculate_asymmetric_errors: bool = False)
Write current state of the fit to file. Unlike to to_file this does not contain information regarding how the fit is constructed - this is because for complex fit objects a reconstruction from e.g. YAML may not work. In such cases the fit object should be contructed via Python and save_state and load_state should be used.
- set_all_parameter_values(param_value_list)
Set all the fit parameters at the same time.
- set_parameter_values(**param_name_value_dict)
Set the fit parameters to new values. Valid keyword arguments are the names of the declared fit parameters.
- Parameters:
param_name_value_dict – new parameter values
- to_file(filename, file_format=None, calculate_asymmetric_errors=False)
Write kafe2 object to file
- property total_cor_mat
the total correlation matrix
- property total_cov_mat
the total covariance matrix
- property total_cov_mat_inverse
inverse of the total covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
- property total_error
array of pointwise total uncertainties
- class kafe2.fit._base.FitEnsembleBase
Bases:
objectObject for generating ensembles of fits to pseudo-data generated according to the specified uncertainty model.
This is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fit ensembles.
- FIT_TYPE = None
- class kafe2.fit._base.FunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)
Bases:
FileIOMixin,objectBase class for function formatter objects. Requires further specialization for each type of model function. Objects derived from this class store information relevant for constructing plain-text and/or LaTeX string representations of functions.
For this, the function name, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, as well as a list of references to
ParameterFormatterobjects which contain information on how to format the model function arguments is stored.Optionally, plain-text/LaTeX expression strings can be provided. These are strings representing the model function expression (i.e. mathematical formula).
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters:
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
- DEFAULT_EXPRESSION_STRING = None
- DEFAULT_LATEX_EXPRESSION_STRING = None
- property arg_formatters
The list of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting all model function arguments.- Return type:
- property expression_format_string
A plain-text-formatted expression for the function. This function will replace all function parameters with their corresponding strings. For example the string “{a}*{x}+{b}” will turn into “A*x + B” when the name of the parameter a was set to “A”, and the name of b is set to “B”.
- Return type:
- get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)
Get a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters:
with_par_values (bool) – If
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f(a=1, b=2, ...)).n_significant_digits (int) – Number of significant digits for rounding.
format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.with_expression (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function.
- property latex_expression_format_string
A LaTeX-formatted expression for the function. This function will replace all function parameters with their corresponding latex string. For example the string
"{a}{x}+{b}"will turn into"A_0 x + B"when the latex name of the parameterawas set to"A_0", and the latex name ofbis set to"B".- Return type:
- property par_formatters
List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting the fit parameters, excluding the independent parameter(s).- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit._base.ModelFunctionBase(model_function=<function linear_model>, independent_argcount=1)
Bases:
FileIOMixin,objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all model functions.
In order to be used as a model function, a native Python function must be wrapped by an object whose class derives from this base class. There is a dedicated
ModelFunctionspecialization for each type of data container.This class provides the basic functionality used by all
ModelFunctionobjects. These use introspection (inspect) for determining the parameter structure of the model function and to ensure the function can be used as a model function (validation).Construct
ModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters:
model_function – function handle
independent_argcount (int) – The amount of independent variables for this model. The first n variables of the model function will be treated as independent variables and will not be fitted.
- FORMATTER_TYPE
alias of
ModelFunctionFormatter
- property argcount
The number of arguments the model function accepts. (including any independent variables which are not parameters)
- property defaults
The default values for model function parameters as a list
- property defaults_dict
The default values for model function parameters as a dict
- property formatter
The
ModelFunctionFormatter-derived object for this function
- property func
The underlying model function handle
- property name
The model function name (a valid Python identifier)
- property parameter_names
The names of the parameters.
- property parameters_with_good_defaults
- property parcount
The number of fitting parameters in the model function.
- property signature
The model function argument specification, as returned by
inspect.signature
- property source_code
- property x_name
The name of the independent variable.
Nonefor 0 independent variables.
- class kafe2.fit._base.ModelFunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)
Bases:
FunctionFormatterA formatter class for model functions.
This object stores the function name, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, as well as a list of references to
ParameterFormatterobjects which contain information on how to format the model function arguments. Additionally formatting information about the independent variable is stored.Optionally, plain-text/LaTeX expression strings can be provided. These are strings representing the model function expression (i.e. mathematical formula).
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters:
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
- get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)
Create a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters:
with_par_values (bool) – If
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f(a=1, b=2, ...)).n_significant_digits (int) – number of significant digits for rounding
format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.with_expression (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function.
- Returns:
The formatted string representing this model function.
- Return type:
- property par_formatters
List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting the fit parameters, excluding the independent parameter(s).- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter(arg_name, value=None, error=None, asymmetric_error=None, name=None, latex_name=None)
Bases:
FileIOMixin,objectFormatter class for model parameter objects.
These objects store the relevant information for constructing plain-text and/or LaTeX string representations of model function parameters.
For this, the original argument name, the name for representation, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, its value and its uncertainty is stored.
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a Parameter Formatter.
- Parameters:
arg_name (str) – A plain string indicating the parameter’s signature inside the function call.
value (float or None) – The parameter value.
error (float or None) – The symmetric parameter error.
asymmetric_error (tuple[float, float] or None) – The asymmetric parameter errors.
name (str or None) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the parameter name.
latex_name (str or None) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the parameter name.
- Return type:
- property asymmetric_error
Tuple containing the asymmetric parameter errors.
- property fixed
If the parameter has been fixed by the user.
Truewhen it’s fixed,Falsewhen not.- Return type:
- get_formatted(value=None, with_name=False, with_value=True, with_errors=True, n_significant_digits=2, round_value_to_error=True, asymmetric_error=False, format_as_latex=False)
Get a formatted string representing this model parameter.
- Parameters:
with_name (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter name.with_value (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter value.with_errors (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter error(s).n_significant_digits (int) – Number of significant digits for rounding.
round_value_to_error (bool) – If
True, the parameter value will be rounded to the same precision as the uncertainty.asymmetric_error (bool) – If
True, the asymmetric parameter uncertainties are used.format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.
- Returns:
The string representation of the parameter.
- Return type:
- class kafe2.fit._base.ParametricModelBaseMixin(model_func, model_parameters, *args, **kwargs)
Bases:
objectA “mixin” class for representing a parametric model. Inheriting from this class in addition to a data container class additionally stores a Python function handle referring to the model function. The argument structure of this function must be compatible with the data container type and it must return a numpy array of the same shape as the
dataproperty of the data container.This mixin class introduces an additional
parametersproperty for the object, which can be used to obtain and set the values of the parameterDerived classes should inherit from
ParametricModelBaseMixinand the relevant data container (in that order).Mixin constructor: sets and initialized the model function.
- Parameters:
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
- MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE
alias of
ModelFunctionBase
- property ndf
- property parameters
Model parameter values
- class kafe2.fit._base.Plot(fit_objects, separate_figures=False)
Bases:
objectThis is a class implementing the creation of Fits from one of more subclasses of :py:obj`PlotAdapterBase`. Consequently a
Plotobject manages one or severalmatplotlibfigures. It controls the overall figure layout and is responsible for axes, subplot and legend management.- Parameters:
fit_objects (int or
FitBaseor Sequence[FitBase]) – which kafe2 fits to use for the plot. A positive integer is interpreted as the fit with the given index that has been performed (with wrappers) since the program started. A negative integer -n is interpreted as the last n fits. kafe2 fit objects are used directly. If a sequence of fit objects is passed they can be displayed as part of the same plot.separate_figures (bool) – whether the fits should be displayed in separate figures.
- FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_CHI2 = '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n $\\hookrightarrow \\chi^2 \\, \\mathrm{{probability =}}${chi2_probability}\n'
- FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_NOT_SATURATED = '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${cost}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n'
- FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_SATURATED = '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n'
- property axes
A list of dictionaries (one per figure) mapping names to
matplotlibAxes objects contained in this figure.
- customize(plot_type, keyword, values)
Set values for keyword arguments used for plots with type plot_type.
This is a convenience wrapper around set_keywords.
The keyword will be passed to the plot adapter method responsible for plotting the plot_type as a keyword argument with a value taken from values. If a default value for keyword is configured, it is overridden.
The values can be specified in two ways:
as a list with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance. The special value
'__skip__'can be used to skip fit objects.as a list of tuples of the form
(index, value), where index denotes the index of the fit object for which the value should be used.
Passing the following special values for a keyword will have the following effects:
'__del__': the value will be removed from the keyword arguments. This includes default values, meaning that the plot call will be made without the keyword argument even if a default value for it exists.'__default__': the customized value will be replaced by the default value.'__skip__': the keywords for this fit will not be changed.
Note
No keyword/value validation is done: everything is passed to the underlying plot methods as specified. Incorrect or incompatible keywords may be ignored or lead to errors.
As an example, to override the labels shown in the legend entries for the data
p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', 'label', ['My Data Label', 'Another Data Label'])
To set keywords for a single fit, pass values as
(index, value), where index is the index of the fit object:p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', 'label', [(1, 'Another Data Label')])
- Parameters:
plot_type (str) – keyword identifying the plot type for which to set a custom keyword argument
keyword (str) – the keyword argument. The corresponding value in values will be passed to the plot adapter method using this keyword argument
values (list of values or list of 2-tuples like
(index, value)) – values that the keyword argument should take for each fit. Can be a list of values with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance, or a list of tuples of the form(index, value)
- Returns:
this Plot instance
- Return type:
Plot
- property figures
The
matplotlibfigures managed by this object.
- get_keywords(plot_type)
Retrieve keyword arguments for plots with type plot_type as they would be used when calling plot.
This is an advanced function. An understanding of how plotting with matplotlib and the PlotAdapter classes in kafe2 work is recommended.
The plot_type must be one of the plot types registered in the PlotAdapter (e.g.
'data','model_line'etc.).
- plot(legend=True, fit_info=True, asymmetric_parameter_errors=False, ratio=False, ratio_range=None, ratio_height_share=0.25, residual=False, residual_range=None, residual_height_share=0.25, pull=False, pull_range=None, pull_height_share=0.25, plot_width_share=0.5, font_scale=1.0, figsize=None)
Plot data, model (and other subplots) for all child
Fitobjects.- Parameters:
legend (bool or Collection[bool]) – if
True, a legend is renderedfit_info – If
True, fit results will be shown in the legend. This can also be a list of booleans, corresponding to the fits handled by thisPlot-object.asymmetric_parameter_errors – if
True, parameter errors in fit results will be asymmetricratio – if
True, a secondary plot containing data/model ratios is shown below the main plotratio_range (tuple of 2 floats) – the y range to set in the secondary plot
ratio_height_share (float) – share of the total height to be taken up by the secondary plot
plot_width_share (float) – share of the total width to be taken up by the plot(s)
font_scale (float) – multiply font size by this amount.
figsize (tuple of 2 floats) – the (width, height) of the figure (in inches) or
Noneto use default
- Returns:
dictionary containing information about the plotted objects
- Return type:
- save(fname=None, figures='all', *args, **kwargs)
Saves the plot figures to files. args and kwargs are passed on to matplotlib.Figure.savefig() .
- set_keywords(plot_type, keyword_spec)
Set values for keyword arguments used for plots with type plot_type.
This is an advanced function. An understanding of how plotting with matplotlib and the PlotAdapter classes in kafe2 work is recommended.
The plot_type must be one of the plot types registered in the PlotAdapter (e.g.
'data','model_line'etc.).The keyword_spec contains dictionaries whose contents will be passed as keyword arguments to the plot adapter method responsible for plotting the plot_type. If keyword spec contains a key for which a default value is configured, it will be overridden.
Passing the following special values for a keyword will have the following effects:
'__del__': the value will be removed from the keyword arguments. This includes default values, meaning that the plot call will be made without the keyword argument even if a default value for it exists.'__default__': the customized value will be replaced by the default value.
Note
No keyword/value validation is done: everything is passed to the underlying plot methods as specified. Incorrect or incompatible keywords may be ignored or lead to errors.
As an example, to override the labels shown in the legend entries for the data
p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', [dict(label='My Data Label'), dict(label='Another Data Label')])
To set keywords for a single fit, pass values as
(index, value), where index is the index of the fit object:p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', [(1, dict(label='Another Data Label'))])
- Parameters:
plot_type (str) – keyword identifying the plot type for which to set a custom keyword argument
keyword_spec (list of values or list of 2-tuples like
(index, value)) – specification of dictionaries containing the keyword arguments to use for fit. Can be either a list of dictionaries with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance, or a list of tuples of the form(index, dict), whereindexdenotes the index of the fit object for which the dictionary dict should be used.
- Returns:
this Plot instance
- Return type:
Plot
- static show(*args, **kwargs)
Convenience wrapper for matplotlib.pyplot.show()
- property x_label
The x-label(s) of the plot. If multiple fits are handled by this plot this is a list of strings. Multiple labels will be separated by a comma in the final plot while skipping duplicates. If a label is
Noneor'__del__'it will be removed. :type: str or list[str]
- property x_range
The plotting x-range for each fit handled by this
Plotobject. :param: List of tuples containing the x_ranges for each fit. :type: list[tuple[float, float]] or tuple[float, float]
- property x_scale
The x-scale for each fit used for creating the support values when plotting and axis scaling. :type: list[str] or str
- property x_ticks
- property y_label
The y-label(s) of the plot. If multiple fits are handled by this plot this is a list of strings. Multiple labels will be separated by a comma in the final plot while skipping duplicates. If a label is
Noneor'__del__'it will be removed. :type: str or list[str]
- property y_range
The plotting y-range for each fit handled by this
Plotobject. :param: List of tuples containing the y_ranges for each fit. :type: list[tuple[float, float]] or tuple[float, float]
- property y_scale
The y-scale for each fit used when plotting. :type: list[str] or str
- property y_ticks
- class kafe2.fit._base.PlotAdapterBase(fit_object, from_container=False)
Bases:
objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of plot adapters.
A
PlotAdapterobject can be constructed for aFitobject of the corresponding type. Its main purpose is to provide an interface for accessing data stored in theFitobject, for the purposes of plotting. Most importantly, it provides methods to call the relevantmatplotlibmethods for plotting the data, model (and other information, depending on the fit type), and constructs the arrays required by these routines in a meaningful way.Classes derived from
PlotAdapterBasemust at the very least contain properties for constructing the x and y point arrays for both the data and the fitted model, as well as methods calling thematplotlibroutines doing the actual plotting.Construct a
PlotAdapterfor aFitobject:- Parameters:
fit_object (kafe2.fit._base.FitBase) – An object derived from
FitBasefrom_container (bool) – Whether fit_object was created ad-hoc from just a data container.
- AVAILABLE_X_SCALES = ('linear',)
- AVAILABLE_Y_SCALES = ('linear', 'log')
- PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE = 'default'
- PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES = {'data': {'container_valid': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'hide': True, 'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'pull': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_pull', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'pull'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'residual': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_residual', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'residual'}}
- call_plot_method(plot_type, target_axes, **kwargs)
Call the registered plot method for plot_type.
- abstract property data_xerr
The magnitude of the data x error bars (used by
plot_data).- Return type:
- abstract property data_yerr
The magnitude of the data y error bars (used by
plot_data).- Return type:
- property from_container
Whether the contained fit object was created ad-hoc from just a data container.
- get_formatted_model_function(**kwargs)
return model function string
- property model_function_parameter_formatters
The model function parameter formatters, excluding the independent variable.
- abstract property model_x
The x coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- abstract property model_xerr
The magnitude of the model x error bars (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- abstract property model_y
The y coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- abstract property model_yerr
The magnitude of the model y error bars (used by
plot_model).- Return type:
- abstractmethod plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)
Method called by the main plot routine to plot the data points to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibtarget axes.- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- abstractmethod plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)
Method called by the main plot routine to plot the model to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibtarget axes.- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_pull(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the pull of the data values on the model to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_ratio(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- plot_residual(target_axes, error_contributions=('data',), **kwargs)
Plot the residuals to a
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject.- Parameters:
target_axes (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The
matplotlibaxes used for plotting.error_contributions (str or Tuple[str]) – Which error contributions to include when plotting the data. Can either be
data,'model'or both.kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments accepted by
matplotlib.pyplot.errorbar.
- Returns:
plot handle(s)
- update_plot_kwargs(plot_type, plot_kwargs)
Update the value of keyword arguments plot_kwargs to be passed to the plot method for for plot_type.
If a keyword argument should be removed, the value of the keyword in plot_kwargs can be set to the special value
'__del__'. To indicate that the default value should be used, the special value'__default__'can be set as a value.
- property x_label
The x axis label of the fit handled by this plot adapter. If
'__del__'is used, the label will be set toNone.- Return type:
- property x_scale
The x axis scale. Available scales are given in
AVAILABLE_X_SCALES- Return type:
- property x_ticks
- property y_label
The x axis label of the fit handled by this plot adapter. If
'__del__'is used, the label will be set toNone.- Return type:
- property y_scale
The y axis scale. Available scales are given in
AVAILABLE_Y_SCALES- Return type:
- property y_ticks
- class kafe2.fit._base.ScalarFormatter(sigma, n_significant_digits=2)
Bases:
objectFormat a scalar to a specified precision, according to the uncertainty.
- kafe2.fit._base.kc_plot_style(data_type, subplot_key, property_key)
Additional functionality: tools
Likelihood Scans and Contours: contours_profiler
- class kafe2.fit.tools.contours_profiler.ContoursProfiler(fit_object, profile_points=100, profile_subtract_min=True, profile_bound=2.45, contour_points=100, contour_sigma_values=None, contour_cl_values=None, contour_smoothing_sigma=0.0, contour_method_kwargs=None)
Bases:
objectObject dedicated to profiling the cost function in one or two parameters.
Once a fit has converged and the cost function is at its minimum, the technique of profiling can be applied to examine the behavior of the cost function around its minimum. Profiling involves repeating the cost function minimization with the value of one particular parameter being fixed to a series of points in the vicinity of the minimum. The function resulting from mapping the parameter values to the cost function value thus obtained, is known as a profile in that parameter.
In two dimensions, two parameters can be profiled simultaneously. The resulting profiles are functions of two variables and can be visualized in the plane by drawing the 3D contours along which this function remains constant.
This object offers a means of calculating both profiles and contours
Construct a
ContoursProfilerobject:- Parameters:
fit_object (
FitBase-derived object) – fit object for which to calculate profiles/contoursprofile_points (int) – number of points at which to sample each profile
profile_subtract_min (bool) – if
True, the value of the cost function at the minimum is subtracted from the profiles, so that only the difference to the minimum is plottedprofile_bound (float) – sample the profile at most this far from the minimum (in sigma)
contour_points (int) – number of points at which to sample each contour
contour_sigma_values (iterable of float) – evaluate and show contours for these confidence levels (specified as sigma)
contour_cl_values (iterable or float) – evaluate and show contours for these confidence levels (specified as probability)
contour_smoothing_sigma (float) – apply a smoothing Gaussian filter with this sigma parameter to each contour (default is
0.0, meaning no smoothing)
- property figures
The
matplotlibfigures managed by this object.
- static show(*args, **kwargs)
Convenience wrapper for matplotlib.pyplot.show()
- get_profile(parameter, low=None, high=None, sigma=None, cl=None, points=None, subtract_min=None)
Calculate and return a profile of the cost function in a parameter.
- Parameters:
parameter (str) – name of the parameter to profile (referred to as x here).
low (float or None) – Lower bound for the profile.
high (float or None) – Upper bound for the profile.
sigma (float) – Number of std deviations to deviate at least from the optimal value in either direction if low or high aren’t defined.
cl (float or None) – Confidence level of the profiled region. If low or high is defined then cl is interpreted as the confidence level of a one-sided confidence interval. If both low and high are undefined then cl is interpreted as the confidence level of the central confidence interval. Cannot be defined if both high and low are defined.
points (int) – number of equidistant points to use as x values
bound (int or tuple of int) – parameter region for the profile. A single value is interpreted as a sigma value for an interval symmetric around the cost function minimum. A tuple of two values is interpreted as the bounds of an arbitrary x interval to be profiled.
- Subtract_min:
if the minimal cost function value should be subtracted from the profile y values.
- Returns:
two-dimensional array of x (parameter) values and y (cost function) values
- Return type:
two-dimensional array of float
- get_contours(parameter_1, parameter_2, smoothing_sigma=None)
Calculate and return a list of contours (one for each requested sigma value).
- Parameters:
- Returns:
list of tuples of the form (sigma, contour)
- Return type:
list of 2-tuples of float and 2d-array
- plot_profile(parameter, low=None, high=None, sigma=None, cl=None, target_axes=None, show_parabolic=True, show_grid=True, show_legend=True, show_fit_minimum=True, show_error_span=True, show_ticks=True, label_ticks_in_sigma=True, label_fit_minimum=True, font_scale=1.0, sigma_steps=1.0)
Plot the profile cost function for a parameter.
- Parameters:
parameter (str) – name of the parameter to profile in
low (float or Sequence[float] or None) – Lower bound(s) at which to display confidence levels.
high (float or Sequence[float] or None) – Upper bound(s) at which to display confidence levels.
sigma (float) – Number of std deviations to deviate at least from the optimal value in either direction if low or high aren’t defined.
cl (float or Sequence[float] or None) – Confidence level(s) to mark in the plot. If low or high is defined then cl is interpreted as the confidence level(s) of one-sided confidence intervals. If both low and high are undefined then cl is interpreted as the confidence level(s) of central confidence intervals. Cannot be defined if both high and low are defined.
target_axes (
matplotlibAxesorNone) –Axesobject (ifNone, a new figure is created)show_parabolic (bool`) – if
True, a parabolic approximation of the profile near the minimum is also drawnshow_grid (bool) – if
True, a grid is drawnshow_legend (bool) – if
True, the legend is displayedshow_fit_minimum (bool) – if
True, the fit minumum is shown as a marker with error barsshow_error_span (bool) – if
True, the parameter error region is shadedshow_ticks (bool :param label_ticks_in_sigma: if
True, label ticks are in units of 1 sigma) – ifTrue, x and y ticks are displayedlabel_fit_minimum (bool) – if
True, the parameter value and the 1 sigma error will be shown as an annotationfont_scale (float) – multiply font size by this amount.
sigma_steps (float) – Stepsize of the ticks in profile and contour plots in units of sigma.
- Returns:
figure containing the plot result
- Return type:
matplotlib.figure.Figure
- plot_contours(parameter_1, parameter_2, target_axes=None, show_grid=True, show_legend=True, show_fit_minimum=True, show_ticks=True, label_ticks_in_sigma=True, naming_convention='sigma', font_scale=1.0, sigma_steps=1.0)
Plot the contour for a parameter pair.
- Parameters:
parameter_1 (str) – name of the parameter appearing on the x axis
parameter_2 (str) – name of the parameter appearing on the y axis
target_axes (
matplotlibAxes` or ``None) –Axesobject (ifNone, a new figure is created)show_grid (bool) – if
True, a grid is drawnshow_legend (bool) – if
True, the legend is displayedshow_fit_minimum (bool) – if
True, the fit minimum is shown as a marker with error barsshow_ticks (bool) – if
True, x and y ticks are displayedlabel_ticks_in_sigma (bool) – if
True, label ticks are in units of 1 sigmanaming_convention (str) – if
'sigma'the contour is labelled in sigma, if'cl'the contour is labelled in confidence levelfont_scale (float) – multiply font size by this amount.
sigma_steps (float) – Stepsize of the ticks in profile and contour plots in units of sigma.
- Returns:
figure containing the plot result
- Return type:
matplotlib.figure.Figure
- plot_profiles_contours_matrix(parameters=None, show_grid_for=None, show_ticks_for='all', show_fit_minimum_for='contours', show_legend=True, show_parabolic_profiles=True, show_error_span_profiles=False, full_matrix=False, label_ticks_in_sigma=True, contour_naming_convention='sigma', font_scale=1.0, sigma_steps=1.0)
Plot all profiles and contours to subplots arranges in a matrix-like fashion.
- Parameters:
parameters (list of parameter names or
None) – parameters for which to display profiles and contours. IfNone, all parameters.show_grid_for (
None,'profiles','contours'or'all') – subplots for which to show a gridshow_ticks_for (
None,'profiles','contours'or'all') – subplots for which to show ticksshow_fit_minimum_for (
None,'profiles','contours'or'all') – subplots for which to show the fit minimumshow_legend (bool) – if
True, the legend is displayedshow_parabolic_profiles (bool) – if
True, a parabolic approximation of the profile near the minimum is also drawnshow_error_span_profiles (bool) – if
True, the parameter uncertainty region is shaded in the profile plotsfull_matrix (bool) – if
True, contour subplots are also shown above the main diagonallabel_ticks_in_sigma (bool) – if
True, label ticks are in units of 1 sigmacontour_naming_convention (str) – if
'sigma'the contour is labelled in sigma, if'cl'the contour is labelled in confidence levelfont_scale (float) – multiply font size by this amount.
sigma_steps (float) – Stepsize of the ticks in profile and contour plots in units of sigma.
- Returns:
figure containing the plot result
- Return type:
matplotlib.figure.Figure
- save(fname=None, figures='all', *args, **kwargs)
Saves the profile figures to files. args and kwargs are passed on to matplotlib.Figure.savefig() .