API documentation¶
This page contains documentation which was automatically extracted from docstrings attached to the kafe2 source code. All major classes, methods and functions provided by kafe2 are documented here. For further information, or if in doubt about the exact functionality, users are invited to consult the source code itself. If you notice a mistake in the kafe2 documentation, or if you think that a particular part needs to be better documented, please open an issue on the kafe2 GitHub page.
kafe2 in a nutshell¶
Parameter estimation tools: fit¶
The kafe2.fit module provides an essential toolkit for estimating model
parameters from data (“fitting”).
It distinguishes between a number of different data types:
series of indexed measurements (dedicated submodule:
indexed),xy data (dedicated submodule:
xy), andhistograms (dedicated submodule:
histogram)
Each of the above data types has its own particularities when it comes to fitting. The main difference is due to the way uncertainties can be defined and interpreted for each type of data.
Indexed data¶
For indexed data, one data set consists of a list of 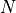 distinct measurements
distinct measurements
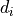 , with the (discrete) index
, with the (discrete) index 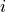 ranging from
ranging from 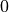 to
to 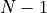 .
For each measurement in the series, one or more uncertainty sources can be defined,
each being a numerical estimate of how much the respective measurement fluctuates.
Correlations between uncertainties on separate measurements
.
For each measurement in the series, one or more uncertainty sources can be defined,
each being a numerical estimate of how much the respective measurement fluctuates.
Correlations between uncertainties on separate measurements 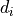 and
and 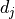 can also
be taken into account by using covariance/correlation matrices.
can also
be taken into account by using covariance/correlation matrices.
Fits to indexed data take these uncertainties and correlations into account when estimating
the model parameters and their uncertainties. When plotting indexed data, measurements are
represented as data points with error bars at 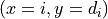 , whereas the model
is indicated by a horizontal line near the corresponding data point.
, whereas the model
is indicated by a horizontal line near the corresponding data point.
The following objects are provided for handling indexed data, as described above:
IndexedContainer: data container for storing indexed dataIndexedParametricModel: corresponding model:uses a model function (
IndexedModelFunction) to calculate the model predictions and stores the result in anIndexedContainer
IndexedFit: a fit of a parametric model to indexed data:finds the minimum of the cost function to find the parameter values for which the model best fits the data
XY data¶
For xy data, the same principle as for indexed data applies, except each measurement and model prediction
now depends on a continuous real independent variable 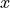 instead of a discrete index
instead of a discrete index 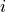 .
In effect, the data now consist of
.
In effect, the data now consist of 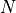 ordered pairs
ordered pairs 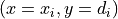 .
.
In contrast to indexed data, where only uncertainties on the measurement could be defined,
for xy data there is the additional possibility of defining additional uncertainites on 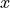 .
These can be handled in a number of different ways when fitting an xy model to data.
When plotting the result of xy fits, the model function is displayed as a continuous
function of
.
These can be handled in a number of different ways when fitting an xy model to data.
When plotting the result of xy fits, the model function is displayed as a continuous
function of 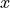 , and an error band can be computed to reflect the model uncertainty,
as determined by propagating the data uncertainties.
, and an error band can be computed to reflect the model uncertainty,
as determined by propagating the data uncertainties.
The following objects are provided for handling xy data:
XYContainer: data container for storing xy dataXYParametricModel: corresponding model:uses a model function (
XYModelFunction) to calculate the model predictions and stores the result in anXYContainer
XYFit: a fit of a parametric model to xy data:finds the minimum of the cost function to find the parameter values for which the model best fits the data
Histograms¶
Finally, kafe2 is also able to handle histograms. Histograms organize measurements whose
values can fall anywhere across a continuum of values into a number of discrete regions
or “bins”. Typically, the continuous “measurement space” (a closed real interval ![[x_{\rm min}, x_{\rm max}]](../../_images/math/c9809eca2b8d4eda10847f0c117804f3b2ac3074.png) )
is subdivided into a sequence of successive intervals at the “bin edges”
)
is subdivided into a sequence of successive intervals at the “bin edges”
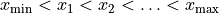 . Whenever a measurement falls into one of the bins, the
value of that histogram bin is incremented by one.
So a histogram is completely defined by its bin edges and the bin values.
. Whenever a measurement falls into one of the bins, the
value of that histogram bin is incremented by one.
So a histogram is completely defined by its bin edges and the bin values.
Note
The bin numbering starts at 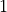 for the first bin and ends at
for the first bin and ends at 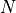 , where
, where 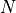 is defined as the size of the histogram. The bin numbers
is defined as the size of the histogram. The bin numbers  and
and 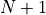 refer to the
underflow (below
refer to the
underflow (below  ) and overflow bin (above
) and overflow bin (above  ), respectively.
), respectively.
Defining a parametric model for histograms is not as straightforward as for xy and indexed data. Seeing as they keep track of the number of entries in different intervals of the continuum, the bin values can be interpreted using probability theory.
As the number of entries approaches infinity, the number of entries 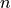 in the bin covering an interval
in the bin covering an interval
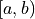 , divided by the total number of entries
, divided by the total number of entries 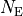 , will approach the probablity of an
event landing in that bin:
, will approach the probablity of an
event landing in that bin:
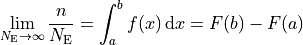
In the above formula, 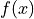 is the probability distribution function (or probability density),
and
is the probability distribution function (or probability density),
and 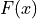 is an antiderivative of
is an antiderivative of 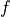 (for example the cumulative probability distribution function).
(for example the cumulative probability distribution function).
Using the above relation, the model prediction 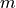 for the bin
for the bin 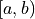 can be defined as:
can be defined as:
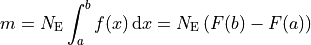
This means that, for histograms, the model density 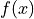 needs to be specified.
The model is then calculated by numerically integrating this function over each bin.
When fitting, however, the model needs to be calculated for many different points in parameter space,
which makes this approach very slow (many numerical integrations until the fit converges).
needs to be specified.
The model is then calculated by numerically integrating this function over each bin.
When fitting, however, the model needs to be calculated for many different points in parameter space,
which makes this approach very slow (many numerical integrations until the fit converges).
An alternative would be to specify the model density antiderviative 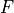 alongside
the model, so that the model can be calculated as a simple difference, rather than a complicated integral.
alongside
the model, so that the model can be calculated as a simple difference, rather than a complicated integral.
The following objects are provided for handling histograms:
HistContainer: data container for storing histogramsHistParametricModel: corresponding model:uses a model function (
HistModelFunction) to calculate the model predictions and stores the result in anHistContainer
HistFit: a fit of a parametric model to histograms:finds the minimum of the cost function to find the parameter values for which the model best fits the data
For creating graphical representations of fits, the Plot is provided. It can be instantiated
with any fit object (or list of fit objects) as an argument and will produce one or more plots accordingly
using matplotlib.
- synopsis
This module contains specialized objects for storing measurement data, defining and fitting parametric models to these data and producing graphical representations (“plots”) of the result. It relies on the
kafe2.coremodule for basic functionality.
Tools for fitting series of indexed measurements (indexed)¶
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of an indexed series of measurements. This can be useful for calculating weighted mean values or template fits.
- synopsis
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of an indexed series of measurements.
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedContainer(data, dtype=<class 'float'>)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.container.DataContainerBaseThis object is a specialized data container for series of indexed measurements.
Construct a container for indexed data:
- Parameters
data (iterable of type <dtype>) – a one-dimensional array of measurements
dtype (type) – data type of the measurements
-
property
size¶ number of data points
-
property
data¶ container data (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
err¶ absolute total data uncertainties (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
cov_mat¶ absolute data covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of absolute data covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix), orNoneif singular
-
property
cor_mat¶ absolute data correlation matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
data_range¶ the minimum and maximum value of the data
- Type
return
-
add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False)¶ Add an uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns
error name
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False)¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns
error name
- Return type
-
exception
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedContainerException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.container.DataContainerException
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunctionConstruct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
cost_function (typing.Callable) – function handle
arg_names (typing.Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_Chi2Base class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
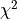 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate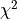 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedFit(data, model_function, cost_function=<kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_Chi2 object>, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to a series of indexed measurements.
- Parameters
data (iterable of float) – the measurement values
model_function (
IndexedModelFunctionor unwrapped native Python function) – the model functioncost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionminimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
-
CONTAINER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainer
-
MODEL_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.indexed.model.IndexedParametricModel
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.indexed.model.IndexedModelFunction
-
PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.indexed.plot.IndexedPlotAdapter
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
IndexedFitException
-
RESERVED_NODE_NAMES= {'cost', 'data', 'data_cor_mat', 'data_cov_mat', 'data_error', 'model', 'model_cor_mat', 'model_cov_mat', 'model_error', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error'}¶
-
property
model¶ array of model predictions for the data points
-
exception
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedFitException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitException
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedModelFunction(model_function)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.model.ModelFunctionBaseConstruct
IndexedModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
model_function – function handle
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
IndexedModelFunctionException
-
FORMATTER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.indexed.format.IndexedModelFunctionFormatter
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedModelFunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, index_name='i', latex_index_name='i', arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.format.FunctionFormatterConstruct a
Formatterfor a model function for indexed data:- Parameters
name – a plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name
latex_name – a LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name
index_name – a plain-text-formatted string representing the index
latex_index_name – a LaTeX-formatted string representing the index
arg_formatters – list of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function argumentsexpression_string – a plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression
latex_expression_string – a LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression
-
get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)¶ Get a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters
with_par_values – if
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f_i(a=1, b=2, ...))n_significant_digits (int) – number of significant digits for rounding
format_as_latex – if
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntaxwith_expression – if
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function
- Returns
string
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedParametricModel(model_func, model_parameters, shape_like=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.model.ParametricModelBaseMixin,kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainerConstruct an
IndexedParametricModelobject:- Parameters
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
shape_like – array with the same shape as the model
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
IndexedModelFunction
-
property
data¶ model predictions (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
data_range¶ tuple containing the minimum and maximum of all model predictions
-
eval_model_function(model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters
model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)- Returns
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type
-
eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(model_parameters=None, par_dx=None)¶ Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the model parameters.
- Parameters
model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)par_dx (float) – step size for numeric differentiation
- Returns
value(s) of the model function derivative for the given parameters
- Return type
-
class
kafe2.fit.indexed.IndexedPlotAdapter(indexed_fit_object)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.plot.PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
IndexedPlotContainerfor aIndexedFitobject:- Parameters
fit_object – an
IndexedFitobject
-
PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE= 'indexed'¶
-
PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES= {'data': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}}¶
-
property
data_x¶ data x values
-
property
data_y¶ data y values
-
property
data_xerr¶ NoneforIndexedPlotContainer- Type
x error bars for data
-
property
data_yerr¶ total uncertainty
- Type
y error bars for data
-
property
model_x¶ model prediction x values
-
property
model_y¶ model prediction y values
-
property
model_xerr¶ x error bars for model (actually used to represent the horizontal step length)
-
property
model_yerr¶ NoneforIndexedPlotContainer- Type
y error bars for model
-
plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the model predictions to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
step_fill_betweenmethod
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_ratio(target_axes, error_contributions='data', **kwargs)¶ Plot the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
Tools for fitting xy data (xy)¶
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of ordered xy pairs. This fit type is used for most cases e.g. when performing fits for the first time or in physics laboratory courses.
- synopsis
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation using data consisting of ordered xy pairs.
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYContainer(x_data, y_data, dtype=<class 'float'>)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainerThis object is a specialized data container for xy data.
Construct a container for xy data:
- Parameters
x_data (iterable of type <dtype>) – a one-dimensional array of measurement x values
y_data (iterable of type <dtype>) – a one-dimensional array of measurement y values
dtype (type) – data type of the measurements
-
property
size¶ number of data points
-
property
data¶ container data (both x and y, two-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
x¶ container x data (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
x_err¶ absolute total data x-uncertainties (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
x_cov_mat¶ absolute data x covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
x_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of absolute data x covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix), orNoneif singular
-
property
x_cor_mat¶ absolute data x correlation matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
y¶
-
property
y_err¶ absolute total data y-uncertainties (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
y_cov_mat¶ absolute data y covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
y_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of absolute data y covariance matrix (
numpy.matrix), orNoneif singular
-
property
y_cor_mat¶ absolute data y correlation matrix (
numpy.matrix)
-
property
x_range¶ x data range
-
property
y_range¶ y data range
-
add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False)¶ Add an uncertainty source for an axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False)¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or
None) – unique name for this uncertainty source. IfNone, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
get_total_error(axis)¶ Get the error object representing the total uncertainty for an axis.
-
property
has_x_errors¶ Trueif at least one x uncertainty source is defined for the data container
-
property
has_uncor_x_errors¶ Trueif at least one x uncertainty source, which is not fully correlated, is defined for the data container
-
property
has_y_errors¶ Trueif at least one x uncertainty source is defined for the data container
-
exception
kafe2.fit.xy.XYContainerException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainerException
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, axes_to_use='xy')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_Chi2Built-in least-squares cost function for xy data.
- Parameters
errors_to_use (
'covariance','pointwise'orNone) – which errors to use when calculating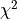
axes_to_use (
'y'or'xy') – take into account errors for which axes
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False, axes_to_use='xy')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYFit(xy_data, model_function=<function linear_model>, cost_function=<kafe2.fit.xy.cost.XYCostFunction_Chi2 object>, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to xy data.
- Parameters
xy_data ((2, N)-array of float) – the x and y measurement values
model_function (
XYModelFunctionor unwrapped native Python function) – the model functioncost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionminimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
-
CONTAINER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.xy.container.XYContainer
-
MODEL_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.xy.model.XYParametricModel
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit._base.model.ModelFunctionBase
-
PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.xy.plot.XYPlotAdapter
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
XYFitException
-
RESERVED_NODE_NAMES= {'cost', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cor_mat_inversex_data_cov_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error', 'x_cor_mat', 'x_cov_mat', 'x_cov_mat_inverse', 'x_error', 'y_data', 'y_data_cor_mat', 'y_data_cov_mat', 'y_data_cov_mat_inverse', 'y_data_error', 'y_model', 'y_model_cor_mat', 'y_model_cov_mat', 'y_model_cov_mat_inverse', 'y_model_error'}¶
-
X_ERROR_ALGORITHMS= ('iterative linear', 'nonlinear')¶
-
property
has_x_errors¶ Trueif at least one x uncertainty source has been defined
-
property
has_y_errors¶ Trueif at least one y uncertainty source has been defined
-
property
x_data¶ array of measurement x values
-
property
x_model¶
-
property
y_data¶ array of measurement data y values
-
property
model¶ (2, N)-array containing x and y model values
-
property
x_data_error¶ array of pointwise x data uncertainties
-
property
y_data_error¶ array of pointwise y data uncertainties
-
property
data_error¶ array of pointwise xy uncertainties (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_data_cov_mat¶ the data x covariance matrix
-
property
y_data_cov_mat¶ the data y covariance matrix
-
property
data_cov_mat¶ the data xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_data_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the data x covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
y_data_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the data y covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
data_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the data xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis,
Noneif singular)
-
property
x_data_cor_mat¶ the data x correlation matrix
-
property
y_data_cor_mat¶ the data y correlation matrix
-
property
data_cor_mat¶ the data xy correlation matrix (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
y_model¶ array of y model predictions for the data points
-
property
x_model_error¶ array of pointwise model x uncertainties
-
property
y_model_error¶ array of pointwise model y uncertainties
-
property
model_error¶ array of pointwise model xy uncertainties (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_model_cov_mat¶ the model x covariance matrix
-
property
y_model_cov_mat¶ the model y covariance matrix
-
property
model_cov_mat¶ the model xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_model_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the model x covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
y_model_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the model y covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
model_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the model xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis,
Noneif singular)
-
property
x_model_cor_mat¶ the model x correlation matrix
-
property
y_model_cor_mat¶ the model y correlation matrix
-
property
model_cor_mat¶ the model xy correlation matrix (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_total_error¶ array of pointwise total x uncertainties
-
property
y_total_error¶ array of pointwise total y uncertainties
-
property
total_error¶ array of pointwise total xy uncertainties (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_total_cov_mat¶ the total x covariance matrix
-
property
y_total_cov_mat¶ the total y covariance matrix
-
property
total_cov_mat¶ the total xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis)
-
property
x_total_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the total x covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
y_total_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the total y covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
total_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the total xy covariance matrix (projected onto the y axis,
Noneif singular)
-
property
x_total_cor_mat¶ the total x correlation matrix
-
property
y_total_cor_mat¶ the total y correlation matrix
-
property
x_range¶ range of the x measurement data
-
property
y_range¶ range of the y measurement data
-
add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data')¶ Add an uncertainty source for axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertaintyreference ('data' or 'model') – which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data')¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertaintyreference ('data' or 'model') – which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
eval_model_function(x=None, model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters
x (iterable of float) – values of x at which to evaluate the model function (if
None, the data x values are used)model_parameters (iterable of float) – the model parameter values (if
None, the current values are used)
- Returns
model function values
- Return type
-
eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(x=None, model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function derivative for each parameter.
- Parameters
x (iterable of float) – values of x at which to evaluate the model function (if
None, the data x values are used)model_parameters (iterable of float) – the model parameter values (if
None, the current values are used)
- Returns
model function values
- Return type
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYFitEnsemble(n_experiments, x_support, model_function, model_parameters, cost_function=<kafe2.fit.xy.cost.XYCostFunction_Chi2 object>, requested_results=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.ensemble.FitEnsembleBaseObject for generating ensembles of fits to xy pseudo-data generated according to the specified uncertainty model.
After constructing an
XYFitEnsembleobject, an error model should be added to it. This is done as forXYFitobjects by using theadd_errororadd_matrix_errormethods.Once an uncertainty model is provided, the fit ensemble can be generated by using the
runmethod. This method starts by generating a pseudo-dataset in such a way that the empirical distribution of the data corresponds to the specified uncertainty model. It then fits the model to the pseudo-data and extracts information from the fit, such as the resulting parameter values or the value of the cost function at the minimum. This is repeated a large number of times in order to evaluate the whole ensemble in a statistically meaningful way.The ensemble result can be visualized by using the
plot_resultsmethod.Construct an
XYFitEnsembleobject.- Parameters
n_experiments (int) – number of pseudoexperiments to perform
x_support (iterable of float) – x values to use as support for calculating the “true” model (“true” x)
model_function (
XYModelFunctionor unwrapped native Python function) – the model functionmodel_parameters (iterable of float) – parameters of the “true” model
cost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionrequested_results (iterable of str) – list of result variables to collect for each toy fit
-
FIT_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.xy.fit.XYFit
-
AVAILABLE_STATISTICS= {'cor_mat': <property object>, 'cov_mat': <property object>, 'kurtosis': <property object>, 'mean': <property object>, 'mean_error': <property object>, 'skew': <property object>, 'std': <property object>}¶
-
property
n_exp¶ the number of pseudo-experiments to perform
-
property
n_par¶ the number of parameters
-
property
n_dat¶ the number of degrees of freedom for the fit
-
property
n_df¶ the number of degrees of freedom for the fit
-
add_error(axis, err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data')¶ Add an uncertainty source for axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_val (float or iterable of float) – pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points
correlation (float) – correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points
relative (bool) – if
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertaintyreference ('data' or 'model') – which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(axis, err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data')¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source for an axis to the data container. Returns an error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Parameters
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – one of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'err_val (iterable of float) – the pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given)
relative (bool) – if
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertaintyreference ('data' or 'model') – which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors
- Returns
error id
- Return type
-
run()¶ Perform the pseudo-experiments. Retrieve and store the requested fit result variables.
-
get_results(*results)¶ Return a dictionary containing the ensembles of result variables.
- Parameters
results (iterable of str. Calling without arguments retrieves all collected results.) – names of result variables to retrieve
- Returns
dict
-
get_results_statistics(results='all', statistics='all')¶ Return a dictionary containing statistics (e.g. mean) of the result variables.
- Parameters
results (iterable of str or
'all'(get statistics for all retrieved variables)) – names of retrieved fit variable for which to return statisticsstatistics (iterable of str or
'all'(get all statistics for each retrieved variable)) – names of statistics to retrieve for each result variable
- Returns
dict
-
plot_result_distributions(results='all', show_legend=True)¶ Make plots with histograms of the requested fit variable values across all pseudo-experiments.
- Parameters
results (iterable of str or
'all'(make plots for all retrieved variables)) – names of retrieved fit variable for which to generate plotsshow_legend (bool) – if
True, show a plot legend on each figure
-
plot_result_scatter(results='all', show_legend=True)¶ Make plots with histograms of the requested fit variable values across all pseudo-experiments.
- Parameters
results (iterable of str or
'all'(make plots for all retrieved variables)) – names of retrieved fit variable for which to generate plotsshow_legend (bool) – if
True, show a plot legend on each figure
-
AVAILABLE_RESULTS= {'cost': <property object>, 'parameter_pulls': <property object>, 'x_data': <property object>, 'y_data': <property object>, 'y_model': <property object>, 'y_pulls': <property object>}¶
-
exception
kafe2.fit.xy.XYFitException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitException
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYParametricModel(x_data, model_func=<function linear_model>, model_parameters=[1.0, 1.0])¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.model.ParametricModelBaseMixin,kafe2.fit.xy.container.XYContainerConstruct an
XYParametricModelobject:- Parameters
x_data – array containing the x values supporting the model
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
-
property
data¶ model predictions (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
x¶ model x support values
-
property
y¶ model y values
-
eval_model_function(x=None, model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function.
- Parameters
x (list or
None) – x values of the support points (ifNone, the model x values are used)model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)
- Returns
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type
-
eval_model_function_derivative_by_parameters(x=None, model_parameters=None, par_dx=None)¶ Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the model parameters.
- Parameters
x (list or
None) – x values of the support points (ifNone, the model x values are used)model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)par_dx (float) – step size for numeric differentiation
- Returns
value(s) of the model function derivative for the given parameters
- Return type
-
eval_model_function_derivative_by_x(x=None, model_parameters=None, dx=None)¶ Evaluate the derivative of the model function with respect to the independent variable (x).
- Parameters
x (list or
None) – x values of the support points (ifNone, the model x values are used)model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)dx (float) – step size for numeric differentiation
- Returns
value(s) of the model function derivative
- Return type
-
exception
kafe2.fit.xy.XYParametricModelException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.xy.container.XYContainerException
-
class
kafe2.fit.xy.XYPlotAdapter(xy_fit_object)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.plot.PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
XYPlotContainerfor aXYFitobject:-
PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE= 'xy'¶
-
PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES= {'data': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_error_band': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_error_band', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_line': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_line', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}, 'ratio_error_band': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio_error_band', 'plot_style_as': 'model_error_band', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}}¶
-
property
data_x¶ data x values
-
property
data_y¶ data y values
-
property
data_xerr¶ total x uncertainty
- Type
x error bars for data
-
property
data_yerr¶ total y uncertainty
- Type
y error bars for data
-
property
model_x¶ model x values
-
property
model_y¶ model y values
-
property
model_xerr¶ NoneforIndexedPlotContainer- Type
x error bars for model
-
property
model_yerr¶ total model uncertainty
- Type
y error bars for model
-
property
model_line_x¶ x support values for model function
-
property
model_line_y¶ y values at support points for model function
-
property
y_error_band¶ one-dimensional array representing the uncertainty band around the model function
-
plot_data(target_axes, error_contributions='data', **kwargs)¶ Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model(target_axes, error_contributions='model', **kwargs)¶ Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model_line(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the model function to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibplotmethod
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model_error_band(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot an error band around the model model function.
- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibfill_betweenmethod
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_ratio(target_axes, error_contributions='data', **kwargs)¶ Plot the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_ratio_error_band(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot model error band around the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
Tools for fitting histograms (histogram)¶
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from histograms. Currently a histogram needs to be filled with all individual data points. A function for setting the bin heights is available but not recommended, as saving and loading those to and from a file is not yet supported.
- synopsis
This submodule provides the necessary objects for parameter estimation from histograms.
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistContainer(n_bins, bin_range, bin_edges=None, fill_data=None, dtype=<class 'int'>)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainerThis object is a specialized data container for organizing data into histograms.
A histogram is a compact representation of a potentially large number of entries which are distributed along a continuum of values. Histograms divide the continuum into intervals (“bins”) and count the number of entries per interval.
Construct a histogram:
- Parameters
n_bins (int) – number of bins
bin_range (tuple of floats) – the lower and upper edges of the entire histogram
bin_edges (list of floats) – the bin edges (if
None, each bin will have the same width)fill_data (list of floats) – entries to fill into the histogram
dtype (type) – data type of histogram entries
-
property
size¶ the number of bins (excluding underflow and overflow bins)
-
property
n_entries¶ the number of entries
-
property
data¶ the number of entries in each bin
-
property
raw_data¶ the number of entries in each bin
-
property
low¶ the lower edge of the histogram
-
property
high¶ the upper edge of the histogram
-
property
bin_range¶ a tuple containing the lower and upper edges of the histogram
-
property
overflow¶ the number of entries in the overflow bin
-
property
underflow¶ the number of entries in the underflow bin
-
property
n_bins¶ the number of bins
-
property
bin_edges¶ a list of the bin edges (including the outermost ones)
-
property
bin_widths¶ a list of the bin widths
-
property
bin_centers¶ a list of the (geometrical) bin centers
-
fill(entries)¶ Fill new entries into the histogram.
- Parameters
entries (list of floats) – list of entries
-
rebin(new_bin_edges)¶ Change the histogram binning.
- Parameters
new_bin_edges (list of float) – list of new bin edges in ascending order
-
set_bins(bin_heights, underflow=0, overflow=0)¶ Set the bin heights according to a pre-calculated histogram :param bin_heights: Heights of the bins :type bin_heights: list of int :param underflow: Number of entries in the underflow bin :type underflow: int :param overflow: Number of entries in the overflow bin :type overflow: int
-
exception
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistContainerException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.indexed.container.IndexedContainerException
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunctionConstruct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
cost_function (typing.Callable) – function handle
arg_names (typing.Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_Chi2Base class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
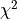 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate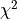 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistCostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihoodBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistFit(data, model_density_function=<function normal_distribution_pdf>, cost_function=<kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihood object>, bin_evaluation='simpson', minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitBaseConstruct a fit of a model to a histogram. If bin_evaluation is a Python function or of a numpy.vectorize object it is interpreted as the antiderivative of model_density_function. If bin_evaluation is equal to “rectangle”, “midpoint”, “trapezoid”, or “simpson” the bin heights are evaluated according to the corresponding quadrature formula. If bin_evaluation is equal to “numerical” the bin heights are evaluated by numerically integrating model_density_function.
- Parameters
data (
HistContainer) – aHistContainerrepresenting histogrammed datamodel_density_function (
HistModelFunctionor unwrapped native Python function) – the model density functioncost_function (
CostFunctionBase-derived or unwrapped native Python function) – the cost functionbin_evaluation (str, callable, or numpy.vectorize) – how the model evaluates bin heights.
minimizer (None, "iminuit", "tminuit", or "scipy".) – the minimizer to use for fitting.
minimizer_kwargs (dict) – dictionary with kwargs for the minimizer.
-
CONTAINER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.histogram.container.HistContainer
-
MODEL_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.histogram.model.HistParametricModel
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.histogram.model.HistModelFunction
-
PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit.histogram.plot.HistPlotAdapter
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
HistFitException
-
RESERVED_NODE_NAMES= {'cost', 'data', 'data_cor_mat', 'data_cov_mat', 'data_error', 'model', 'model_cor_mat', 'model_cov_mat', 'model_density', 'model_error', 'total_cor_mat', 'total_cov_mat', 'total_error'}¶
-
property
model¶ array of model predictions for the data points
-
eval_model_function_density(x, model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function density.
- Parameters
x (iterable of float) – values of x at which to evaluate the model function density
model_parameters (iterable of float) – the model parameter values (if
None, the current values are used)
- Returns
model function density values
- Return type
-
exception
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistFitException¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.fit.FitException
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistModelFunction(model_density_function=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.model.ModelFunctionBaseConstruct
XYModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
model_density_function – function handle
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
HistModelFunctionException
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistParametricModel(n_bins, bin_range, model_density_func=<function normal_distribution_pdf>, model_parameters=[1.0, 1.0], bin_edges=None, bin_evaluation='simpson')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.model.ParametricModelBaseMixin,kafe2.fit.histogram.container.HistContainerMixin constructor: sets and initialized the model function.
- Parameters
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
HistModelFunction
-
property
data¶ model predictions (one-dimensional
numpy.ndarray)
-
property
bin_evaluation¶ how the model evaluates bin heights. :rtype str, callable, or numpy.vectorize
- Type
return
-
property
bin_evaluation_string¶ string representation of how the model evaluates bin heights. :rtype str
- Type
return
-
eval_model_function_density(x, model_parameters=None)¶ Evaluate the model function density.
- Parameters
x (list of float) – x values of the support points
model_parameters (list or
None) – values of the model parameters (ifNone, the current values are used)
- Returns
value(s) of the model function for the given parameters
- Return type
-
fill(entries)¶ Fill new entries into the histogram.
- Parameters
entries (list of floats) – list of entries
-
class
kafe2.fit.histogram.HistPlotAdapter(hist_fit_object)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.plot.PlotAdapterBaseConstruct an
HistPlotContainerfor aHistFitobject:- Parameters
fit_object – an
HistFitobjectn_plot_points_model_density – number of plot points to use for plotting the model density
-
PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE= 'histogram'¶
-
PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES= {'data': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model_density': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model_density', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}}¶
-
property
data_x¶ data x values
-
property
data_y¶ data y values
-
property
data_xerr¶ x error bars for data (actually used to represent the bins)
-
property
data_yerr¶ total uncertainty
- Type
y error bars for data
-
property
model_x¶ model prediction x values
-
property
model_y¶ model prediction y values
-
property
model_xerr¶ x error bars for model (actually used to represent the bins)
-
property
model_yerr¶ NoneforHistPlotContainer- Type
y error bars for model
-
property
model_density_x¶ x support points for model density plot
-
property
model_density_y¶ value of model density at the support points
-
plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the measurement data to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethoderrorbar
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the model predictions to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodbar
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_model_density(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Plot the model density to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
plot_ratio(target_axes, error_contributions='data', **kwargs)¶ Plot the data/model ratio to a specified
matplotlibAxesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobjectkwargs – keyword arguments accepted by the
matplotlibmethodserrorbarorplot
- Returns
plot handle(s)
Abstract base classes (_base)¶
- synopsis
This submodule contains the abstract base classes for all objects used by the
kafe2.fitmodule.
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction(cost_function, arg_names=None, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectBase class for cost functions. Built from a Python function with some extra functionality used by Fit objects.
Any Python function returning a
floatcan be used as a cost function, although a number of common cost functions are provided as built-ins for all fit types.In order to be used as a model function, a native Python function must be wrapped by an object whose class derives from this base class. There is a dedicated
CostFunctionspecialization for each type of fit.This class provides the basic functionality used by all
CostFunctionobjects. These use introspection (inspect) for determining the parameter structure of the cost function and to ensure the function can be used as a cost function (validation).Construct
CostFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
cost_function (typing.Callable) – function handle
arg_names (typing.Iterable[str]) – the names to use for the cost function arguments. If None, detect from function signature.
add_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
CostFunctionException
-
property
name¶ The cost function name (a valid Python identifier)
-
property
func¶ The cost function handle
-
property
arg_names¶ The names of the cost function arguments.
-
property
formatter¶ The
Formatterobject for this function
-
property
argument_formatters¶ The
Formatterobjects for the function arguments
-
property
needs_errors¶ Whether the cost function needs errors for a meaningful result
-
property
is_chi2¶ Whether the cost function is a chi2 cost function.
-
property
saturated¶ Whether the cost function value is calculated from a saturated likelihood.
-
goodness_of_fit(*args)¶ How well the model agrees with the data.
-
chi2_probability(cost_function_value, ndf)¶ The chi2 probability associated with this cost function, None for non-chi2 cost functions.
-
get_uncertainty_gaussian_approximation(data)¶ Get the gaussian approximation of the uncertainty inherent to the cost function, returns 0 by default.
- Parameters
data – the fit data
- Returns
the approximated gaussian uncertainty given the fit data
-
is_data_compatible(data)¶ Tests if model data is compatible with cost function
- Parameters
data (numpy.ndarray) – the fit data
- Returns
if the data is compatible, and if not a reason for the incompatibility
- Return type
(boo, str)
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.CostFunctionFormatter(name, name_saturated=None, latex_name=None, latex_name_saturated=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.format.FunctionFormatterA Formatter class for Cost Functions.
Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
-
property
name_saturated¶ A plain-text-formatted string indicating the saturated function name.
- Return type
-
property
latex_name_saturated¶ A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the saturated function name.
- Return type
-
get_formatted(value=None, n_degrees_of_freedom=None, with_name=True, saturated=False, with_value_per_ndf=True, format_as_latex=False)¶ Get a formatted string representing this cost function.
- Parameters
value (float or None) – Value of the cost function (if not
None, the returned string will include this).n_degrees_of_freedom (int or None) – Number of degrees of freedom (if not
None, the returned string will include this).with_name (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the cost function namesaturated (bool) – If
True, the cost function name for the saturated Likelihood will be used (no effect for chi2).with_value_per_ndf (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the value-ndf ratio as a decimal valueformat_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax
- Return type
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction_Chi2(errors_to_use='covariance', fallback_on_singular=True, add_constraint_cost=True)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunctionBase class for built-in least-squares cost function.
- Parameters
errors_to_use (str or None) – Which errors to use when calculating
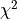 .
Either
.
Either 'covariance','pointwise'orNone.fallback_on_singular (bool) – If
Trueand the covariance matrix is singular (or the errors are zero), calculate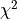 as with
as with errors_to_use=Noneadd_constraint_cost (bool) – If
True, automatically add the cost for kafe2 constraints.
-
chi2_no_errors(data, model)¶ A least-squares cost function calculated from y data and model values, without considering uncertainties:
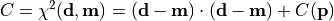
In the above,
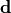 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
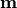 are the model predictions,
and
are the model predictions,
and 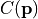 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.- Parameters
data – measurement data
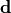
model – model predictions
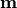
- Returns
cost function value
-
chi2_covariance(data, model, total_cov_mat_inverse)¶ A least-squares cost function calculated from y data and model values, considering the covariance matrix of the y measurements.

In the above,
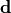 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
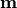 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
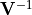 is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
and
is the inverse of the total covariance matrix,
and 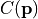 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.- Parameters
data – measurement data
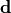
model – model predictions
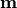
total_cov_mat_inverse – inverse of the total covariance matrix
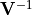
- Returns
cost function value
-
chi2_pointwise_errors(data, model, total_error)¶ A least-squares cost function calculated from y data and model values, considering pointwise (uncorrelated) uncertainties for each data point:
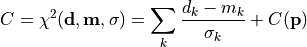
In the above,
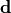 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
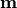 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
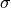 are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and
are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and 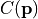 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.- Parameters
data – measurement data
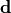
model – model predictions
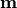
total_error – total error vector
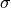
- Returns
cost function value
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.CostFunction_NegLogLikelihood(data_point_distribution='poisson', ratio=False)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.cost.CostFunctionBase class for built-in negative log-likelihood cost function.
In addition to the measurement data and model predictions, likelihood-fits require a probability distribution describing how the measurements are distributed around the model predictions. This built-in cost function supports two such distributions: the Poisson and Gaussian (normal) distributions.
In general, a negative log-likelihood cost function is defined as the double negative logarithm of the product of the individual likelihoods of the data points.
The likelihood ratio is defined as ratio of the likelihood function for each individual observation, divided by the so-called marginal likelihood.
- Parameters
-
static
nll_gaussian(data, model, total_error)¶ A negative log-likelihood function assuming Gaussian statistics for each measurement.
The cost function is given by:
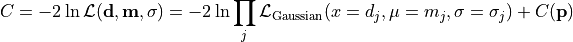
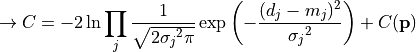
In the above,
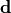 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
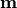 are the model predictions,
are the model predictions,
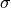 are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and
are the pointwise total uncertainties,
and 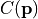 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.- Parameters
data – measurement data
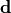
model – model predictions
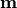
total_error – total error vector
- Returns
cost function value
-
static
nll_poisson(data, model)¶ A negative log-likelihood function assuming Poisson statistics for each measurement.
The cost function is given by:
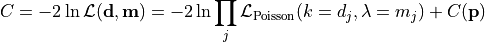
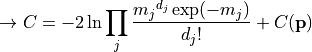
In the above,
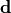 are the measurements,
are the measurements,
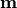 are the model predictions,
and
are the model predictions,
and 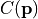 is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.
is the additional cost resulting from any constrained parameters.- Parameters
data – measurement data
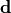
model – model predictions
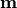
- Returns
cost function value
-
static
nllr_gaussian(data, model, total_error)¶
-
static
nllr_poisson(data, model)¶
-
is_data_compatible(data)¶ Tests if model data is compatible with cost function
- Parameters
data (numpy.ndarray) – the fit data
- Returns
if the data is compatible, and if not a reason for the incompatibility
- Return type
(boo, str)
-
get_uncertainty_gaussian_approximation(data)¶ Get the gaussian approximation of the uncertainty inherent to the cost function, returns 0 by default.
- Parameters
data – the fit data
- Returns
the approximated gaussian uncertainty given the fit data
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.DataContainerBase¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of data containers.
It stores measurement data and uncertainties.
-
property
axis_labels¶ The axis labels describing the dataset.
-
abstract property
data¶ A numpy array containing the data values.
- Return type
-
abstract property
err¶ A numpy array containing the pointwise data uncertainties.
- Return type
-
abstract property
cov_mat¶ A numpy matrix containing the covariance matrix of the data.
- Return type
-
abstract property
cov_mat_inverse¶ obj`None` if not invertible).
- Return type
- Type
A numpy matrix containing inverse of the data covariance matrix (or
- Type
py
-
property
has_errors¶ Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for the data container.- Return type
-
add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference=None)¶ Add an uncertainty source to the data container.
- Parameters
err_val (float or numpy.ndarray[float]) – Pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (typing.Iterable[float] or None) – The data values to use when computing absolute errors from relative ones (and vice-versa)
- Returns
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference=None)¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source to the data container.
- Parameters
err_matrix – Covariance or correlation matrix.
matrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'.name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If :py:obj`None`, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.
err_val (typing.Iterable[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given).
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (typing.Iterable[float] or None) – the data values to use when computing absolute errors from relative ones (and vice-versa)
- Returns
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type
-
disable_error(error_name)¶ Temporarily disable an uncertainty source so that it doesn’t count towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters
error_name (str) – error name
-
enable_error(error_name)¶ (Re-)Enable an uncertainty source so that it counts towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters
error_name (str) – error name
-
get_matching_errors(matching_criteria=None, matching_type='equal')¶ Return a list of uncertainty objects fulfilling the specified matching criteria.
- Valid keys for matching_criteria:
name(the unique error name)type(eithersimpleormatrix)correlated(bool, only matches simple errors!)relative(bool)
Note
The error objects contained in the dictionary are not copies, but the original error objects. Modifying them is possible, but not recommended. If you do modify any of them, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be done by calling the private method
_clear_total_error_cache.- Parameters
matching_criteria (dict or None) – Key-value pairs specifying matching criteria. The resulting error array will only contain error objects matching all provided criteria. If
None, all error objects are returned.matching_type (str) – How to perform the matching. If
'equal', the value in matching_criteria is checked for equality against the stored value. If'regex', the value in matching_criteria is interpreted as a regular expression and is matched against the stored value.
- Returns
Dict mapping error name to
GaussianErrorBase-derived error objects.- Return type
-
get_error(error_name)¶ Return the uncertainty object holding the uncertainty.
Note
If you modify this object, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be forced by calling
enable_error.- Parameters
error_name (str) – error name
- Returns
error object
- Return type
kafe2.core.error.GaussianErrorBase
-
get_total_error()¶ Get the error object representing the total uncertainty.
- Returns
error object representing the total uncertainty
- Return type
kafe2.core.error.MatrixGaussianError
-
property
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.FitBase(data, model_function, cost_function, minimizer=None, minimizer_kwargs=None, dynamic_error_algorithm='nonlinear')¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fitters.
This is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fits.
- Parameters
-
CONTAINER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit._base.container.DataContainerBase
-
MODEL_TYPE= None¶
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE= None¶
-
PLOT_ADAPTER_TYPE= None¶
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
FitException
-
RESERVED_NODE_NAMES= None¶
-
property
data¶ array of measurement values
-
property
data_error¶ array of pointwise data uncertainties
-
property
data_cov_mat¶ the data covariance matrix
-
property
data_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the data covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
data_cor_mat¶ the data correlation matrix
-
property
data_container¶ The data container used in this fit.
- Return type
-
abstract property
model¶
-
property
model_error¶ array of pointwise model uncertainties
-
property
model_cov_mat¶ the model covariance matrix
-
property
model_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the model covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
model_cor_mat¶ the model correlation matrix
-
property
total_error¶ array of pointwise total uncertainties
-
property
total_cov_mat¶ the total covariance matrix
-
property
total_cov_mat_inverse¶ inverse of the total covariance matrix (or
Noneif singular)
-
property
total_cor_mat¶ the total correlation matrix
-
property
model_function¶ The wrapped model function as a
ModelFunctionBaseor derived object. This object contains the model function as well as formatting information used for this fit.- Return type
-
property
parameter_values¶ The current parameter values.
- Return type
-
property
parameter_errors¶ The current parameter uncertainties.
- Return type
-
property
parameter_cov_mat¶ The current parameter covariance matrix.
- Return type
-
property
parameter_cor_mat¶ The current parameter correlation matrix.
- Return type
-
property
asymmetric_parameter_errors¶ The current asymmetric parameter uncertainties.
- Return type
-
property
parameter_name_value_dict¶ A dictionary mapping each parameter name to its current value.
-
property
parameter_constraints¶ The gaussian constraints given for the fit parameters.
- Return type
list[kafe2.core.constraint.GaussianSimpleParameterConstraint or kafe2.core.constraint.GaussianMatrixParameterConstraint]
-
property
has_model_errors¶ Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for the model.- Return type
-
property
has_data_errors¶ Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for the data.- Return type
-
property
has_errors¶ Trueif at least one uncertainty source is defined for either the data or the model.- Return type
-
property
model_count¶ The number of model functions contained in the fit, 1 by default.
- Return type
-
property
goodness_of_fit¶
-
property
dynamic_error_algorithm¶ The algorithm to use for handling errors that depend on the model parameters. :rtype: str
-
property
chi2_probability¶ The chi2 probability for the current model values.
-
set_parameter_values(**param_name_value_dict)¶ Set the fit parameters to new values. Valid keyword arguments are the names of the declared fit parameters.
- Parameters
param_name_value_dict – new parameter values
-
set_all_parameter_values(param_value_list)¶ Set all the fit parameters at the same time.
- Parameters
param_value_list (typing.Iterable[float]) – List of parameter values (mind the order).
-
fix_parameter(name, value=None)¶ Fix a parameter so that its value doesn’t change when calling
do_fit.- Parameters
name (str) – The name of the parameter to be fixed
or None value (float) – The value to be given to the fixed parameter. If
Nonethe current value fromparameter_valueswill be used.
-
release_parameter(name)¶ Release a fixed parameter so that its value once again changes when calling
do_fit.- Parameters
name (str) – The name of the fixed parameter to be released
-
limit_parameter(name, lower=None, upper=None)¶ Limit a parameter to a given range.
-
unlimit_parameter(name)¶ Unlimit a parameter.
- Parameters
name (str) – The name of the parameter to unlimit.
-
add_matrix_parameter_constraint(names, values, matrix, matrix_type='cov', uncertainties=None, relative=False)¶ Advanced class for applying correlated constraints to several parameters of a fit. The order of names, values, matrix, and uncertainties must be aligned. In other words the first index must belong to the first value, the first row/column in the matrix, etc.
Let N be the number of parameters to be constrained.
- Parameters
names (typing.Collection[str]) – The names of the parameters to be constrained. Must be of shape (N,).
values (typing.Sized[float]) – The values to which the parameters should be constrained. Must be of shape shape (N,).
matrix (typing.Iterable[float]) – The matrix that defines the correlation between the parameters. By default interpreted as a covariance matrix. Can also be interpreted as a correlation matrix by setting matrix_type. Must be of shape shape (N, N).
matrix_type (str) – Either
'cov'or'cor'. Defines whether the matrix should be interpreted as a covariance matrix or as a correlation matrix.uncertainties (None or typing.Iterable[float]) – The uncertainties to be used in conjunction with a correlation matrix. Must be of shape (N,)
relative (bool) – Whether the covariance matrix/the uncertainties should be interpreted as relative to values.
-
add_parameter_constraint(name, value, uncertainty, relative=False)¶ Apply a simple gaussian constraint to a single fit parameter.
- Parameters
name (str) – The name of the parameter to be constrained.
value (float) – The value to which the parameter should be constrained.
uncertainty (float) – The uncertainty with which the parameter should be constrained to the given value.
relative (bool) – Whether the given uncertainty is relative to the given value.
-
get_matching_errors(matching_criteria=None, matching_type='equal')¶ Return a list of uncertainty objects fulfilling the specified matching criteria.
- Valid keys for matching_criteria:
name(the unique error name)type(either'simple'or'matrix')correlated(bool, only matches simple errors!)reference(either'model'or'data')
Note
The error objects contained in the dictionary are not copies, but the original error objects. Modifying them is possible, but not recommended. If you do modify any of them, the changes will not be reflected in the total error calculation until the error cache is cleared. This can be done by calling the private dataset method
_clear_total_error_cache.- Parameters
matching_criteria (dict or None) – Key-value pairs specifying matching criteria. The resulting error array will only contain error objects matching all provided criteria. If
None, all error objects are returned.matching_type (str) – How to perform the matching. If
'equal', the value in matching_criteria is checked for equality against the stored value. If'regex', the value in matching_criteria is interpreted as a regular expression and is matched against the stored value.
- Returns
Dict mapping error name to
GaussianErrorBase-derived error objects.- Return type
-
add_error(err_val, name=None, correlation=0, relative=False, reference='data', **kwargs)¶ Add an uncertainty source to the fit.
- Parameters
err_val (float or typing.Iterable[float]) – Pointwise uncertainty/uncertainties for all data points.
name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.correlation (float) – Correlation coefficient between any two distinct data points.
relative (bool) – If
True, err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Either
'data'or'model'. Specifies which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors.
- Returns
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type
-
add_matrix_error(err_matrix, matrix_type, name=None, err_val=None, relative=False, reference='data', **kwargs)¶ Add a matrix uncertainty source for use in the fit.
- Parameters
err_matrix – covariance or correlation matrix
matrix_type (str) – One of
'covariance'/'cov'or'correlation'/'cor'name (str or None) – Unique name for this uncertainty source. If
None, the name of the error source will be set to a random alphanumeric string.err_val (typing.Iterable[float]) – The pointwise uncertainties (mandatory if only a correlation matrix is given).
relative (bool) – If
True, the covariance matrix and/or err_val will be interpreted as a relative uncertainty.reference (str) – Either
'data'or'model'. Specifies which reference values to use when calculating absolute errors from relative errors.
- Returns
An error id which uniquely identifies the created error source.
- Return type
-
disable_error(err_id)¶ Temporarily disable an uncertainty source so that it doesn’t count towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters
err_id (str) – error id
-
enable_error(err_id)¶ (Re-)Enable an uncertainty source so that it counts towards calculating the total uncertainty.
- Parameters
err_id (str) – error id
-
do_fit(asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)¶ Perform the minimization of the cost function.
-
assign_model_function_name(name)¶ Assign a string to be the model function name.
- Parameters
name (str) – The new name.
-
assign_model_function_expression(expression_format_string)¶ Assign a plain-text-formatted expression string to the model function.
- Parameters
expression_format_string (str) – The plain text string.
-
assign_parameter_names(**par_names_dict)¶ Assign display strings to all model function arguments.
- Parameters
par_names_dict – Dictionary mapping the parameter names to their display names.
-
assign_model_function_latex_name(latex_name)¶ Assign a LaTeX-formatted string to be the model function name.
- Parameters
latex_name (str) – The LaTeX string.
-
assign_model_function_latex_expression(latex_expression_format_string)¶ Assign a LaTeX-formatted expression string to the model function.
- Parameters
latex_expression_format_string (str) – The LaTeX string. Elements like
'{par_name}'will be replaced automatically with the corresponding LaTeX names for the given parameter. These can be set withassign_parameter_latex_names.
-
assign_parameter_latex_names(**par_latex_names_dict)¶ Assign LaTeX-formatted strings to all model function arguments.
- Parameters
par_latex_names_dict – Dictionary mapping the parameter names to their latex names.
-
get_result_dict(asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)¶ Return a dictionary of the fit results.
-
report(output_stream=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='UTF-8'>, show_data=True, show_model=True, show_fit_results=True, asymmetric_parameter_errors=False)¶ Print a summary of the fit state and/or results.
- Parameters
output_stream (io.TextIOBase) – The output stream to which the report should be printed.
show_data (bool) – If
True, print out information about the data.show_model (bool) – If
True, print out information about the parametric model.show_fit_results (bool) – If
True, print out information about the fit results.asymmetric_parameter_errors (bool) – If
True, use two different parameter errors for up/down directions.
-
to_file(filename, file_format=None, calculate_asymmetric_errors=False)¶ Write kafe2 object to file
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.FitEnsembleBase¶ Bases:
objectObject for generating ensembles of fits to pseudo-data generated according to the specified uncertainty model.
This is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of fit ensembles.
-
FIT_TYPE= None¶
-
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.FunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectBase class for function formatter objects. Requires further specialization for each type of model function. Objects derived from this class store information relevant for constructing plain-text and/or LaTeX string representations of functions.
For this, the function name, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, as well as a list of references to
ParameterFormatterobjects which contain information on how to format the model function arguments is stored.Optionally, plain-text/LaTeX expression strings can be provided. These are strings representing the model function expression (i.e. mathematical formula).
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
-
DEFAULT_EXPRESSION_STRING= None¶
-
DEFAULT_LATEX_EXPRESSION_STRING= None¶
-
property
expression_format_string¶ A plain-text-formatted expression for the function. This function will replace all function parameters with their corresponding strings. For example the string “{a}*{x}+{b}” will turn into “A*x + B” when the name of the parameter a was set to “A”, and the name of b is set to “B”.
- Return type
-
property
latex_expression_format_string¶ A LaTeX-formatted expression for the function. This function will replace all function parameters with their corresponding latex string. For example the string
"{a}{x}+{b}"will turn into"A_0 x + B"when the latex name of the parameterawas set to"A_0", and the latex name ofbis set to"B".- Return type
-
property
arg_formatters¶ The list of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting all model function arguments.- Return type
-
property
par_formatters¶ List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting the fit parameters, excluding the independent parameter(s).- Return type
-
get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)¶ Get a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters
with_par_values (bool) – If
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f(a=1, b=2, ...)).n_significant_digits (int) – Number of significant digits for rounding.
format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.with_expression (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function.
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.ModelFunctionBase(model_function=<function linear_model>, independent_argcount=1)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all model functions.
In order to be used as a model function, a native Python function must be wrapped by an object whose class derives from this base class. There is a dedicated
ModelFunctionspecialization for each type of data container.This class provides the basic functionality used by all
ModelFunctionobjects. These use introspection (inspect) for determining the parameter structure of the model function and to ensure the function can be used as a model function (validation).Construct
ModelFunctionobject (a wrapper for a native Python function):- Parameters
model_function – function handle
independent_argcount (int) – The amount of independent variables for this model. The first n variables of the model function will be treated as independent variables and will not be fitted.
-
EXCEPTION_TYPE¶ alias of
ModelFunctionException
-
FORMATTER_TYPE¶ alias of
kafe2.fit._base.format.ModelFunctionFormatter
-
property
name¶ The model function name (a valid Python identifier)
-
property
func¶ The underlying model function handle
-
property
signature¶ The model function argument specification, as returned by
inspect.signature
-
property
argcount¶ The number of arguments the model function accepts. (including any independent variables which are not parameters)
-
property
parcount¶ The number of fitting parameters in the model function.
-
property
x_name¶ The name of the independent variable.
Nonefor 0 independent variables.
-
property
formatter¶ The
ModelFunctionFormatter-derived object for this function
-
property
defaults¶ The default values for model function parameters as a list
-
property
defaults_dict¶ The default values for model function parameters as a dict
-
property
source_code¶
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.ModelFunctionFormatter(name, latex_name=None, arg_formatters=None, expression_string=None, latex_expression_string=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit._base.format.FunctionFormatterA formatter class for model functions.
This object stores the function name, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, as well as a list of references to
ParameterFormatterobjects which contain information on how to format the model function arguments. Additionally formatting information about the independent variable is stored.Optionally, plain-text/LaTeX expression strings can be provided. These are strings representing the model function expression (i.e. mathematical formula).
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a formatter for a model function:
- Parameters
name (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function name.
latex_name (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function name.
arg_formatters (list[kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter]) – List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects, formatters for function arguments.expression_string (str) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the function expression.
latex_expression_string (str) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the function expression.
-
property
par_formatters¶ List of
ParameterFormatter-derived objects used for formatting the fit parameters, excluding the independent parameter(s).- Return type
-
get_formatted(with_par_values=False, n_significant_digits=2, format_as_latex=False, with_expression=False)¶ Create a formatted string representing this model function.
- Parameters
with_par_values (bool) – If
True, output will include the value of each function parameter (e.g.f(a=1, b=2, ...)).n_significant_digits (int) – number of significant digits for rounding
format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.with_expression (bool) – If
True, the returned string will include the expression assigned to the function.
- Returns
The formatted string representing this model function.
- Return type
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.ParameterFormatter(arg_name, value=None, error=None, asymmetric_error=None, name=None, latex_name=None)¶ Bases:
kafe2.fit.io.file.FileIOMixin,objectFormatter class for model parameter objects.
These objects store the relevant information for constructing plain-text and/or LaTeX string representations of model function parameters.
For this, the original argument name, the name for representation, formatted as a plain-text/LaTeX string, its value and its uncertainty is stored.
The formatted string is obtained by calling the
get_formattedmethod.Construct a Parameter Formatter.
- Parameters
arg_name (str) – A plain string indicating the parameter’s signature inside the function call.
asymmetric_error (tuple[float, float] or None) – The asymmetric parameter errors.
name (str or None) – A plain-text-formatted string indicating the parameter name.
latex_name (str or None) – A LaTeX-formatted string indicating the parameter name.
- Return type
-
property
asymmetric_error¶ Tuple containing the asymmetric parameter errors.
-
property
fixed¶ If the parameter has been fixed by the user.
Truewhen it’s fixed,Falsewhen not.- Return type
-
get_formatted(with_name=False, with_value=True, with_errors=True, n_significant_digits=2, round_value_to_error=True, asymmetric_error=False, format_as_latex=False)¶ Get a formatted string representing this model parameter.
- Parameters
with_name (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter name.with_value (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter value.with_errors (bool) – If
True, the output will include the parameter error(s).n_significant_digits (int) – Number of significant digits for rounding.
round_value_to_error (bool) – If
True, the parameter value will be rounded to the same precision as the uncertainty.asymmetric_error (bool) – If
True, the asymmetric parameter uncertainties are used.format_as_latex (bool) – If
True, the returned string will be formatted using LaTeX syntax.
- Returns
The string representation of the parameter.
- Return type
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.ParametricModelBaseMixin(model_func, model_parameters, *args, **kwargs)¶ Bases:
objectA “mixin” class for representing a parametric model. Inheriting from this class in addition to a data container class additionally stores a Python function handle referring to the model function. The argument structure of this function must be compatible with the data container type and it must return a numpy array of the same shape as the
dataproperty of the data container.This mixin class introduces an additional
parametersproperty for the object, which can be used to obtain and set the values of the parameterDerived classes should inherit from
ParametricModelBaseMixinand the relevant data container (in that order).Mixin constructor: sets and initialized the model function.
- Parameters
model_func – handle of Python function (the model function)
model_parameters – iterable of parameter values with which the model function should be initialized
-
MODEL_FUNCTION_TYPE¶ alias of
ModelFunctionBase
-
property
ndf¶
-
property
parameters¶ Model parameter values
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.Plot(fit_objects, separate_figures=False)¶ Bases:
objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of plotters.
A
PlotBaseobject manages one or severalmatplotlibfigures that contain plots created from variousFitBase-derived objects.It controls the overall figure layout and is responsible for axes, subplot and legend management.
-
FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_CHI2= '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n $\\hookrightarrow \\chi^2 \\, \\mathrm{{probability =}}${chi2_probability:#.3g}\n'¶
-
FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_SATURATED= '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n'¶
-
FIT_INFO_STRING_FORMAT_NOT_SATURATED= '{model_function}\n{parameters}\n $\\hookrightarrow${cost}\n $\\hookrightarrow${fit_quality}\n'¶
-
property
figures¶ The
matplotlibfigures managed by this object.
-
property
axes¶ A list of dictionaries (one per figure) mapping names to
matplotlibAxes objects contained in this figure.
-
property
x_range¶
-
property
y_range¶
-
plot(legend=True, fit_info=True, asymmetric_parameter_errors=False, ratio=False, ratio_range=None, ratio_height_share=0.25, plot_width_share=0.5, figsize=None)¶ Plot data, model (and other subplots) for all child
Fitobjects.- Parameters
legend – if
True, a legend is renderedfit_info – if
True, fit results will be shown in the legendasymmetric_parameter_errors – if
True, parameter errors in fit results will be asymmetricratio – if
True, a secondary plot containing data/model ratios is shown below the main plotratio_range (tuple of 2 floats) – the y range to set in the secondary plot
ratio_height_share (float) – share of the total height to be taken up by the secondary plot
plot_width_share (float) – share of the total width to be taken up by the plot(s)
figsize (tuple of 2 floats) – the (width, height) of the figure (in inches) or
Noneto use default
- Returns
dictionary containing information about the plotted objects
- Return type
-
get_keywords(plot_type)¶ Retrieve keyword arguments for plots with type plot_type as they would be used when calling plot.
This is an advanced function. An understanding of how plotting with matplotlib and the PlotAdapter classes in kafe2 work is recommended.
The plot_type must be one of the plot types registered in the PlotAdapter (e.g.
'data','model_line'etc.).- Parameters
plot_type (str) – keyword identifying the plot type for which to set a custom keyword argument
- Returns
list of dictionaries (one per fit instance) containing plot keywords and their values
- Return type
list of dict
-
set_keywords(plot_type, keyword_spec)¶ Set values for keyword arguments used for plots with type plot_type.
This is an advanced function. An understanding of how plotting with matplotlib and the PlotAdapter classes in kafe2 work is recommended.
The plot_type must be one of the plot types registered in the PlotAdapter (e.g.
'data','model_line'etc.).The keyword_spec contains dictionaries whose contents will be passed as keyword arguments to the plot adapter method responsible for plotting the plot_type. If keyword spec contains a key for which a default value is configured, it will be overridden.
Passing the following special values for a keyword will have the following effects:
'__del__': the value will be removed from the keyword arguments. This includes default values, meaning that the plot call will be made without the keyword argument even if a default value for it exists.'__default__': the customized value will be replaced by the default value.
Note
No keyword/value validation is done: everything is passed to the underlying plot methods as specified. Incorrect or incompatible keywords may be ignored or lead to errors.
As an example, to override the labels shown in the legend entries for the data
p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', [dict(label='My Data Label'), dict(label='Another Data Label')])
To set keywords for a single fit, pass values as
(index, value), where index is the index of the fit object:p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', [(1, dict(label='Another Data Label'))])
- Parameters
plot_type (str) – keyword identifying the plot type for which to set a custom keyword argument
keyword_spec (list of values or list of 2-tuples like
(index, value)) – specification of dictionaries containing the keyword arguments to use for fit. Can be either a list of dictionaries with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance, or a list of tuples of the form(index, dict), whereindexdenotes the index of the fit object for which the dictionary dict should be used.
- Returns
this Plot instance
- Return type
Plot
-
customize(plot_type, keyword, values)¶ Set values for keyword arguments used for plots with type plot_type.
This is a convenience wrapper around set_keywords.
The keyword will be passed to the plot adapter method responsible for plotting the plot_type as a keyword argument with a value taken from values. If a default value for keyword is configured, it is overridden.
The values can be specified in two ways:
as a list with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance. The special value
'__skip__'can be used to skip fit objects.as a list of tuples of the form
(index, value), where index denotes the index of the fit object for which the value should be used.
Passing the following special values for a keyword will have the following effects:
'__del__': the value will be removed from the keyword arguments. This includes default values, meaning that the plot call will be made without the keyword argument even if a default value for it exists.'__default__': the customized value will be replaced by the default value.'__skip__': the keywords for this fit will not be changed.
Note
No keyword/value validation is done: everything is passed to the underlying plot methods as specified. Incorrect or incompatible keywords may be ignored or lead to errors.
As an example, to override the labels shown in the legend entries for the data
p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', 'label', ['My Data Label', 'Another Data Label'])
To set keywords for a single fit, pass values as
(index, value), where index is the index of the fit object:p = Plot([fit_1, fit_2]) p.customize('data', 'label', [(1, 'Another Data Label')])
- Parameters
plot_type (str) – keyword identifying the plot type for which to set a custom keyword argument
keyword (str) – the keyword argument. The corresponding value in values will be passed to the plot adapter method using this keyword argument
values (list of values or list of 2-tuples like
(index, value)) – values that the keyword argument should take for each fit. Can be a list of values with a length corresponding to the number of fit objects managed by this Plot instance, or a list of tuples of the form(index, value)
- Returns
this Plot instance
- Return type
Plot
-
-
class
kafe2.fit._base.PlotAdapterBase(fit_object, axis_labels=None, None)¶ Bases:
objectThis is a purely abstract class implementing the minimal interface required by all types of plot adapters.
A
PlotAdapterobject can be constructed for aFitobject of the corresponding type. Its main purpose is to provide an interface for accessing data stored in theFitobject, for the purposes of plotting. Most importantly, it provides methods to call the relevantmatplotlibmethods for plotting the data, model (and other information, depending on the fit type), and constructs the arrays required by these routines in a meaningful way.Classes derived from
PlotAdaptermust at the very least contain properties for constructing thexandypoint arrays for both the data and the fitted model, as well as methods calling thematplotlibroutines doing the actual plotting.Construct a
PlotAdapterfor aFitobject:- Parameters
-
PLOT_STYLE_CONFIG_DATA_TYPE= 'default'¶
-
PLOT_SUBPLOT_TYPES= {'data': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_data', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'model': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_model', 'target_axes': 'main'}, 'ratio': {'plot_adapter_method': 'plot_ratio', 'plot_style_as': 'data', 'target_axes': 'ratio'}}¶
-
get_axis_labels()¶ Get the axis labels used with this Plot Adapter.
-
call_plot_method(plot_type, target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Call the registered plot method for plot_type.
-
update_plot_kwargs(plot_type, plot_kwargs)¶ Update the value of keyword arguments plot_kwargs to be passed to the plot method for for plot_type.
If a keyword argument should be removed, the value of the keyword in plot_kwargs can be set to the special value
'__del__'. To indicate that the default value should be used, the special value'__default__'can be set as a value.
-
abstract property
data_xerr¶ The magnitude of the data ‘x’ error bars (used by
plot_data).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract property
data_yerr¶ The magnitude of the data ‘y’ error bars (used by
plot_data).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract property
model_x¶ The ‘x’ coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract property
model_y¶ The ‘y’ coordinates of the model (used by
plot_model).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract property
model_xerr¶ The magnitude of the model ‘x’ error bars (used by
plot_model).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract property
model_yerr¶ The magnitude of the model ‘y’ error bars (used by
plot_model).- Returns
iterable
-
abstract
plot_data(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Method called by the main plot routine to plot the data points to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobject- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
abstract
plot_model(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Method called by the main plot routine to plot the model to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobject- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
abstract
plot_ratio(target_axes, **kwargs)¶ Method called by the main plot routine to plot the data/model ratio to a specified matplotlib
Axesobject.- Parameters
target_axes –
matplotlibAxesobject- Returns
plot handle(s)
-
get_formatted_model_function(**kwargs)¶ return model function string
-
property
model_function_parameter_formatters¶ The model function parameter formatters, excluding the independent variable.
-
kafe2.fit._base.kc_plot_style(data_type, subplot_key, property_key)¶